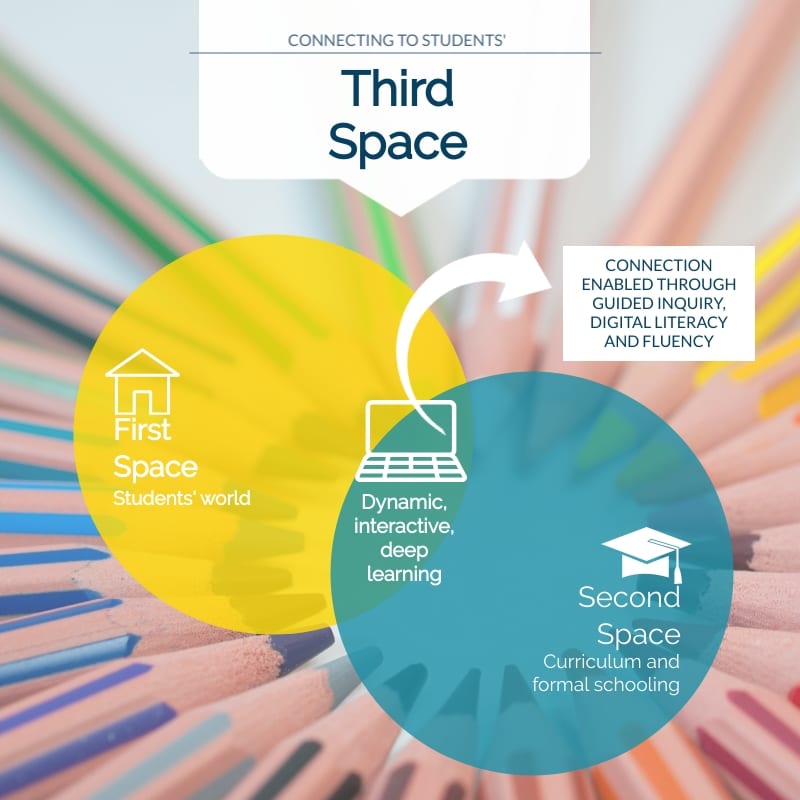
21st century skills can be defined in what seems to be an infinite number of ways. Ultimately, what the definitions have in common are specific skills, process or traits learners require to work and live effectively now and into the future. These include learning skills (4 Cs), literacy skills, and life skills (Thoughtful Learning, 2017). 21st century skills, specifically the 4 C’s, are crucial in the current education climate. Rather than outcomes-based, content-driven curriculum, we see the majority of senior syllabus documents reference and require students to work through inquiry processes, while a minority require a problem-based process. Either way, these processes require students to commit to and utilise the 4 C’s – communication, collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity (Partnership for 21st Century Learning, 2017a). The stages of the inquiry process as outlined by Queensland Curriculum and Assessment Authority (2018) identify reflection as a central cog, constantly interacting with the processes of forming, finding, analysing, and evaluating. Within the overarching inquiry process, students can collaborate to form their inquiry and find valid and reliable evidence, critically analyse, interpret and evaluate their findings, while communicating their ideas. Throughout the entire process students must reflect creatively to try new approaches and revise their process. TLs also work with the general capabilities and cross-curriculum priorities to meet national requirements and embed these practices into learning experiences.
The role of the library in this 21st century space
TLs and school libraries can play a key role in supporting schools in their 21st century endeavours. Taking insight from Partnership for 21st Century Learning’s (2017b) framework, planning for 21st century learning environments involves the following considerations, assessment and accountability, leadership and culture, learning, teaching and professional learning, and infrastructure. TLs provide leadership in learning and professional development and provide environments that nurture 21st learning activities. Furthermore, through collaboration TLs can work across the school network to ensure high-quality assessment is offered and the school program is meeting accountability measures. Currently, with the incoming senior curriculum, our library is supporting the Deputy of Teaching and Learning to map the cognitive verbs across all year levels. The intent is to upskill students in these cognitive processes and ingrain the metalanguage in all years in preparation for the skills required of the senior program. We are using software to record the skills across subject areas and year levels and will then assess gaps and opportunities. Additionally, through our work with Assignment Help Pages and curation of assignment support material, we collaborate with teachers on the development of assessment items. We assist teachers to ensure the assessment aligns with the required achievement outcomes, standard elaborations, and cognitive verbs and where appropriate through a process of inquiry. We support the Centre for Learning Enrichment to develop formative and summative tasks suitable for a variety of learning needs and curate resources to support these specific learning needs. The library environment can also work as a place for this learning, collaboration and assessment to occur. Library spaces should be flexible, engaging, and conducive to 21st century learning. The availability of a range of resources including staff, technology, print resources, and flexible seating areas allows students and teachers to work in more dynamic ways than a traditional classroom. Elliott (2010) describes this type of library as a Learning Commons, whereby students can enquire, create, collaborate and explore. But what’s in a name? Does the name need to be the defining factor? A library can be a learning commons, a place for staff and students to come together and further their learning experiences, without the need for a name change. It’s far more important for the principles and vision to be clear and enacted than for a new name and no action. After all, we want students to go out into the world and engage with libraries beyond the school setting. They need to know that libraries are learning commons and neither are exclusive or separate entities. Nevertheless, sometimes a name change automatically changes perceptions – but there must be substance behind this. The Standards of Practice for School Library Learning Commons in Canada provide a clear framework to guide libraries in the change toward a school-wide learning commons environment (Koechlin, & Sykes, 2014). These standards also clearly reflect 21st century skills. To cater to the needs of the community and future-proof the library space and services, a learning commons approach should be adopted. This way, the library “encourages participatory learning and allows for co-construction of understanding from a variety of sources” (Holland, 2015, para. 3). Schools and classrooms are still isolated spaces where teachers work in isolation. In contrast, a learning commons approach makes teaching and learning visible and collaborative. It’s not about teaching in a fish bowl, rather it is about everyone diving in.
References
Elliott, C. (2010). School library to learning commons: Planning the journey. Synergy, 8(2). Retrieved from http://www.slav.vic.edu.au/synergy/volume-8-number-2-2010/learning-landscapes/82-school-library-to-learning-commons-planning-the-journey.html
Holland, B. (2015). 21st-century libraries: The learning commons. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/blog/21st-century-libraries-learning-commons-beth-holland
Koechlin, C & Sykes, J. (2014). Canadian school libraries leading learning. Synergy, 12(2). Retrieved from http://www.slav.vic.edu.au/synergy/volume-12-number-2-2014/perspectives-global/426-canadian-school-libraries-leading-learning.html
Partnership for 21st Century Learning. (2017a). Above and beyond [Infographic]. Retrieved from http://www.p21.org/storage/documents/4csposter.pdf
Partnership for 21st Century Learning. (2017b). Building your roadmap for 21st century learning environments. Retrieved from http://www.roadmap21.org/
Queensland Curriculum and Assessment Authority. (2018). Senior secondary: A–Z senior subject list. Retrieved from https://www.qcaa.qld.edu.au/senior/a-z-subject-list
Thoughtful Learning. (2017). What are 21st century skills? [FAQ]. Retrieved from https://k12.thoughtfullearning.com/FAQ/what-are-21st-century-skills
[Reflection: Module 4.3]