Tag: 21st Century Learning
Introduction to Social Media – Reflection on INF506 Module 1

OLJ task 1: Social Media and Society – Journal Article Analysis
Self Esteem and Social Media, a Reflection:
I’ve selected the article by Lavrence & Cambre (2020) because it (and a few other of the articles provided) brings up another issue (in addition to those I mentioned in my previous post – not part of this assessment) with social media use: self esteem. The world of online interaction is a reflection of our 3 dimensional ‘real’ world, but it isn’t itself particularly ‘real.’ There has been a lot of research behind the use of magazines and their impact on the self esteems of various people. Men, young men, women, and just people in general. It makes sense therefore for the content to remain influential, despite the mode of delivery changing from printed magazines to electronic forms and social media.
Just as history has been written by the winners and images have been photoshopped and filtered, so too should we expect social media to be rife with filters and propaganda style imagery. To pretend that social media is responsible for the concepts of “raced, gendered, classed, aged, abled” information belies the historical examples of these issues in our society. The only thing that has changed is the mode of delivery and as educators we must help our students be aware of these issues so that they can identify them and discredit or stand up to them where necessary.
I particularly liked the phrase: “(we must) recast validation for appearance as a primary source of female empowerment through ideologies of online visibility” (Lavrence & Cambre, 2020, p.3). In terms of editing ‘selfies,’ I personally find them empowering. I occasionally play with the filters and then take a ‘real’ (unfiltered) photo in order to ground myself. I can generally tell when I need to get more sleep or apply creams to my skin or frizz gel to my hair from these experiences but don’t particularly notice my esteem changing. Nor do I notice my esteem changing when I see digitally enhanced images on the internet. Celeste Barber is a great master at this as well on Instagram – often copying ‘fake’ videos and images with more realistic versions. We still need validation for our appearance, we still need empowerment and we need to recognise different ideologies of online visibility, and we can still do these things with ‘selfies.’
I had not heard of ‘rinsta’ and ‘finsta’ but the concepts are interesting. I like to change photos sometimes because the normal camera filter does not represent the true beauty that I felt in that moment. Sometimes it is a selfie and sometimes it is a sunset. I consider these slightly edited images real, even though I also use the #nofilter on those occasions were the original represented near perfect reality. I think it is important to help our students develop their ‘digital forensic gaze’ (Lavrence & Cambre, 2020, p.11) to help them maintain a more stable self-esteem, particularly those who identify as cis-women, but as we’ve seen in the magazine era, not limited to cis-women.
Introduction to Social Media – Reflection on INF506 Module 1
Is social media good for us, or do we perceive it to be bad based on (possibly) outdated perceptions of healthy interaction?
I’m no stranger to social media. I have accounts on all of the top platforms, although I find Twitter a more boring version of Facebook and rarely check it) and even have my own Facebook group (#teacherswhoknowme). I am, in fact, questioning the benefits given the amount of time I spend on it instead of doing other, more traditionally ‘productive’ activities.
Yet, growing up, I was addicted to reading. I thought nothing of spending entire days in bed reading a stack of books that I checked out from the library, or later in my teens, books I’d bought in used bookstores. I even had a best friend who shared my love of reading and we’d chill in her room for entire weekends reading or going to bookstores and libraries. It seems a weird thing to do now but at the time, it never occurred to us. It probably saved us from the pursuits of boredom that impact teen behaviour today. (e.g. We weren’t hanging out at the shopping mall, smoking cigarettes or creating graffiti, etc).
Furthermore, my brother and I grew up playing outside a lot, as typical in the childhoods of the 1980’s and prior, but I remember when we moved in to live with my dad that my step mother lamented that we spent too much time on the sofa watching TV. What they did not take into account was our ‘social capital’ (Lampe, 2015) had changed. We no longer felt confident to roam outside freely and we preferred to stick together in our new environment. Similarly, the social capital of today’s youth has changed.
Nothing remains static in this world, why should socialising methods? Apart from the need for our society to increase their levels of physical activity to negate the health impacts of a sedentary lifestyle, why shouldn’t we be able to socialise primarily via diverse social media platforms, spending ‘time and effort’ building friendships in this environment, particularly if ‘communication of all forms builds relationships’ (Lampe, 2015).
 This reminds me of the readings on ‘participatory culture’ / 21st century learning skills.
This reminds me of the readings on ‘participatory culture’ / 21st century learning skills.
Another change to society is that social media allows us to have more ‘weak ties’ (Lampe, 2015) with a larger amount of people, building the amount of information to which we have access makes collaboration easier, and improves access to information for those who may have limited access in their physical environments.
Yes, I probably spend ‘too much’ time on Facebook. And I can definitely say that this is related to the stress I feel on particular days, living in a new house that needs renovating in a new town with my children increasingly occupied in their own pursuits and my husband having to commute and spending more time at work. I need the connection and I need it to be familiar. I just need to remember to have a healthy work – life balance!
 (Note: Some colleagues don’t like to use Facebook / social media for work purposes as it has the potential to cross over their work – life balance)
(Note: Some colleagues don’t like to use Facebook / social media for work purposes as it has the potential to cross over their work – life balance)
Social Media and Education
Akcaoglu & Bowman (2016, 2.1) are spot on when they say that the use of Facebook by educators creates “more interest in and perceive(d) more value in course content, (with students feeling) closer to the course and perceive(d) their instructors as more involved.” [However it is important to note that if I try to utilise Facebook in a primary school setting, it will not be for the use of my students as they are all ‘under age’ by the terms and conditions created by Facebook (and Instagram, etc) and I will therefore have to be creative in enabling global connections for my students.]
Personally, I am glad to not have to use the discussion forums anymore as the students waffle on. With Facebook, we are all used to ‘soundbites’ or snippets of information, scrolling on when we see long posts so I’m hopeful the waffling will be minimal with this course. (Save the waffling for your blog, I say!)
 I am also reminded of the readings from Digital Citizenship, where we need to use 21st Century Learning devices for 21st Century learners…
I am also reminded of the readings from Digital Citizenship, where we need to use 21st Century Learning devices for 21st Century learners…
Social media influence and misinformation
Gruzd, Wellman & Mai (2017) offer important points regarding social media, in terms of its influence and misinformation. Advertising (influence) is difficult to spot – in fact, individual people advertise on social media often just as well as corporations – and do so without cost to themselves. YouTube and Instagram have become renown for their social media ‘influencers’ (people who make a living using their personal social media platforms as advertising on behalf of larger corporations and even governments or those with political agendas). ‘Alternative facts’ or misinformation (lies – as I prefer to call them) are now as rife as hidden advertisements on TV, junk mail in the post and spam emails once were. As educators, we must help our students recognise these traits and use social media responsibly!
Link to Glossary of Social Media Terms
References
Akcaoglu, M., & Bowman, N. D. (2016). Using instructor-led Facebook groups to enhance students’ perceptions of course content. Computers in Human Behavior, 65(C), 582-590. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2016.05.029
Gruzd, A., Jacobson, J., Wellman, B., & Mai, P. H. (2017). Social media and society: Introduction to the special issue. American Behavioral Scientist, 61(7), 647-652. doi:10.1177/0002764217717567
Lampe, C. [TEDxTalks]. (2015, April 6). Is social media good for you? TEDxUofM. [Video] https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=po01VlNvCcQ
Lavrence, C., & Cambre, C. (2020). “Do I Look Like My Selfie?”: Filters and the Digital-Forensic Gaze. Social Media + Society. https://doi.org/10.1177/2056305120955182
Best practice for leading and supporting digital citizenship
(Reflecting on my learning in ETL523 Modules 4, 5 & 6)
“Digital leaders understand that we must put real-world tools in the hands of students and allow them to create artefacts of learning that demonstrate conceptual mastery. This is an important pedagogical shift as it focuses on enhancing essential skill sets—communication, collaboration, creativity, media literacy, global connectedness, critical thinking, and problem solving – that society demands….Leaders need to be the catalysts for change…..Digital leadership begins with identifying obstacles to change and specific solutions to overcome them in order to transform schools in the digital age” (Sheninger, 2017).
Notably, in terms of creating a productive digital learning environment, Sheninger (2017) identifies ‘7 pillars for digital leadership in education’ as: communication, public relations, branding, student engagement/learning, professional growth/development, re-envisioning learning spaces and environments, and opportunity.
Rather than avoid global connections and social media, and rather than limit our students (forcing them to go ‘underground’ with a secret world of digital environments of their own making) we need need to learn how to embrace it safely and productively as global digital citizens (Ohler, 2011). We also need our school principals and supervisors to help promote a community of practice and positive learning environments by being “willing to listen, delegate, distribute, empower, and step out of the way of the learning” (Lindsay, 2016, p.110).
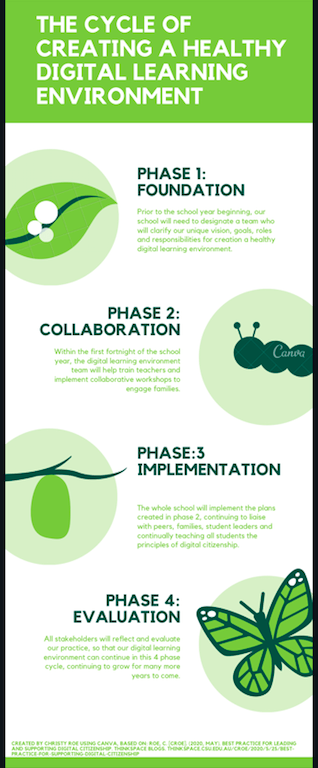
Utilising the readings for modules 4, 5 and 6, as well as a few of my own, following the 6 month multi-phase structure suggested by Chen & Orth (2013), Cofino (2012) and Common Sense Media (n.d.) which begins prior to the start of the school year, we can complete the following 4 phases:
-
Prior to the school year beginning, school contexts need to begin phase 1 by clarifying our unique vision, goals, roles and responsibilities:
- First. form a strong team of information and digital technology leaders (Chen & Orth, 2013; Common Sense Media, n.d.). (See my previous 9 blog posts on creating a school Community of Practice or the evaluation of practice via the 3 blog posts on Quality Teaching Framework/Rounds and also this video on Teacherpreneurs from the Centre for Teaching Quality for motivation!)
- Create and deliver an environmental scan utilising this template for a ‘Situational Analysis’ by Christy Roe (based on suggestions from) the resources provided by Hague & Payton (2010), and/or Pashiardis (1996), particularly as shown in the hexagon images below:
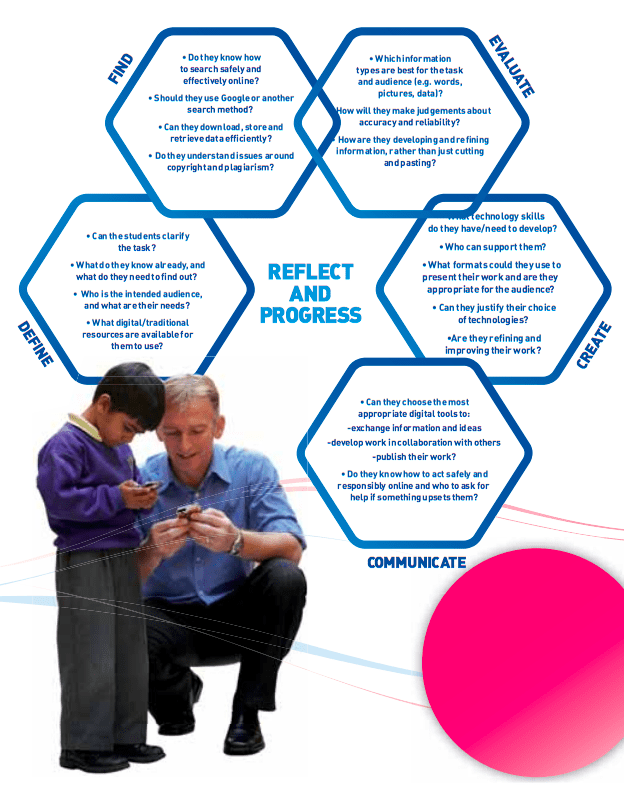
Digital Literacy Planning Tool ‘Reflect & Progress’ image by Hague & Payton, 2010, p.47 - Implement a technology audit (such as this one created by Christy Roe) and/or bullying survey (such as this one created by the University of South Australia) (Chen & Orth, 2013).
- Facilitate the formulation of policies, procedures or guidelines such as an acceptable use policy (using a questionnaire such as this one created by Christy Roe) based on the policy created by the administration (such as those listed in the resources section below), including cohesive terminology that we will utilise as a school (Common Sense Media, n.d.), e.g. linking the Positive Behaviour for Learning Behaviour Matrix or Code of Student Conduct to the school’s “Acceptable use Policy (AUP), Responsible Use Guidelines (RUG), Acceptable Use Agreement (AUA), Internet Use Policy (IUP), Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), or Bring Your Own Technology (BYOT)” etc.
- Liaise with others in our personal learning networks (PLN) (Sheninger, 2017) to map the digital citizenship areas of the syllabus or curriculum documents (NESA / ACARA), find examples of a digital citizenship scope and sequence (such as this (2011) one by Mike Ribble), develop sample lessons or units of work, and accumulate appropriate resources (such as those provided in the resources section below)–made available to all stakeholders (Common Sense Media, n.d.).
- Allow teacher librarians (and the school leadership teams) to readily undertake the role of information leaders who ‘meet the students where they are,’ recognising that there may not only be gaps in terms of technology access, or information access, but there may also be an (intergenerational) gap between what some view as the purpose of technology – i.e. is the purpose of technology to assist in informing, socialising or varying degrees of both, and what is true for the individuals in each school or home context? (Levinson, 2010, p.11).
2. In phase 2, within the first fortnight of the school year, we must train teachers and engage families:
“Alignment between school and home with regards to digital citizenship and healthy digital usage is a hallmark of a 21st-century school. A community-wide understanding of the norms, rules of behaviour, rules of engagement, and common practices is necessary for all schools in order to raise an ethical, digital (and real-life) citizen. Without this key parental partnership, these conversations regarding digital citizenship will just become incoherent whispers in the minds of our students, overwhelmed by the louder voices of media, false information, and misunderstanding” (Chen & Orth, 2013).
- As per the circles image from Hague & Payton (2010) (as well as information from Sheninger (2017)), schools and families need to continually foster 21st century learning and digital literacy skills such as: creativity, (innovation), critical thinking, evaluation (and problem solving), cultural and social understanding, collaboration, effective communication, (global collectedness), the ability to find and select information, (media literacy), e-safety and technological functional skills.
- While at the same time, we must also utilise situations of technology misuse as learning opportunities (see the POISE image below) for the students as well as ourselves as adult digital citizens, setting appropriate boundaries, listening student voices, and continuously encouraging digital literacy and digital citizenship (Chen & Orth, 2013).
- Educators as professionals need to get onboard with 21st century learning and nurture safe, culturally aware, global citizenship and global connections for ourselves as well as for and with our students (Hilt, 2011);
- We must ensure that our digital citizenship curriculum not only protects our students in terms of safety, privacy, copyright, fair use or legality issues, but that it also promotes global cultural, gender, socio-economic status, religion, language and ability awareness and a global appreciation of difference (Hilt, 2011).
- Educators who have embraced the need for global digital citizenship and global connections, need to lead by example and have our own safe, culturally aware, positive and professional ‘brand’ or digital footprint, and we also need to help our students create and tailor their own safe, culturally aware and positive digital footprint ‘brand(s)’ (Neilson, 2012).
- The digital citizenship leadership team, or perhaps even the whole staff, need to hold regular meetings and face to face information and collaboration sessions with families to ensure that preferred means of communication are clarified, that families have input into the digital citizenship program and also so that families are given support in implementing policies, procedures and guidelines at home that suit their individual situation(s) (Chen & Orth, 2013; Levinson, 2010).
- Finally, the digital citizenship team need to develop a plan to help students move from digital citizenship to digital leadership by creating a technology peer mentorship or student technology leadership program (such as YesK12.org) (Oxley, 2012; TeachThought Staff, 2018).
3. In phase 3, we must implement our plans:
- Prior to students being given devices, we must workshop the digital citizenship expectations, policy, procedures and guidelines that we created in phase 1 & 2 (Cofino, 2012).
“The message is threefold: (1) helping children become good digital citizens must be an ongoing practice led by families and schools together; (2) having access to a range of technology and global connections through school creates a positive context in which to have these conversations; and (3) students will make mistakes, and it’s our collective responsibility to turn mistakes into learnable moments” (Chen & Orth, 2013).
-

Bitmoji Christy ‘Do it!’ Once students begin to utilise digital devices, we must implement the digital citizenship lessons or units of work that we created in phase 2, with a key focus on 21st century learning skills, boundaries, student voice, digital footprints and global connections.
- We must implement the peer mentorship program that we created in phase 2, including student voice in the consequences for unacceptable behaviours (such as the student court, implied by in the slideshow by Cofino, 2012).
- We must continually check in with families, using the resources and communication devices agreed upon in phase 2.
4. And finally, in phase 4, we will reflect and evaluate:
![Growth Coaching International (n.d.) Growth Framework [Image]](https://thinkspace.csu.edu.au/croe/files/2020/05/Growth-Coaching-International-n.d.-GROWTH-Framework-Image.jpeg)
List of resources for Teachers and Students:
Policies, procedures or guidelines:
- New South Wales Department of Education and Training’s Policies & procedures > Student use of digital devices and online services (implemented January 27, 2020)
- eSafety Commissioner Teacher Resources;
- State of Victoria (Department of Education & Training) – Consent, Acceptable use agreements and Online services (updated November 2018)
- Sample BYOT Policies http://www.teachthought.com/technology/11-sample-education-byot-policies-to-help-you-create-your-own/
- Sample BYOD Policies http://www.k12blueprint.com/byod
- ‘An overview of school AUP’ written by David Warlick (2008)
- New Zealand Ministry of Education – Digital technology: Safe and responsible use in schools (2015). See also Netsafe.
- Code of Conduct (formerly Digital Citizenship Policy) Garibaldi Secondary School (USA).
- Using digital technologies to support learning and teaching – Victorian State Government, Australia
- Edutopia How to create social media guidelines for your school
- Alberta Canada Social Media Policy for School Districts
Resources for digital citizenship lessons:
- In addition to those recommended in my team’s ETL523 Assessment 2 website, there are also:

5 POISE Tips Infographic PDF by Christy Roe using information from Chen & Orth (2013) - 5 POISE Tips Infographic (shown here) by Christy Roe, based on information from Chen & Orth (2013) for use by both teachers and families
- Common Craft. (2011). Protecting reputations online. http://www.commoncraft.com/video/protecting-reputations-online.
- Common Sense Media. (2010, November 2). Our Connected Culture. http://youtu.be/L0XQj1anI-E
- eSafety Commissioner Cyberbullying resource
- Digital Life Student Intro Video by Common Sense Media, (2010),
- Overexposed
- Attention young professionals! What’s in your digital baggage?
- DontYouForgetAboutMe. (2007, August 11). Everyone – Think before you post (English). http://youtu.be/4w4_Hrwh2XI.
- ‘I Forgot My Phone’ (YouTube | 2:10 mins) | http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OINa46HeWg8 CharstarleneTV. (2013, August 22). I forgot my phone. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OINa46HeWg8.
Examples of global citizenship programs:
- Global Citizen Diploma program
- Lindsay, J. (2009, March 7). Digiteens go global. http://www.slideshare.net/julielindsay/digiteens-go-global (The Digiteens program is no longer running but information is still available about how to implement it).
- Mirtschin, A. (2012, April 26). Hello little world skypers. http://murcha.wordpress.com/2012/04/26/hello-little-world-skypers-group/
- Morgan, L. (2012, March 19). Skype with an astronaut! http://www.frugalteacher.com/2012/03/skyping-with-astronaut.html
- Internet censorship in China [Tag]. New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/search?query=internet%20censorship%20in%20china&sort=best
References and further reading
- Beam, C. (2011). Bootleg nation: How strict are Chinese copyright laws? Slate. http://www.slate.com/articles/news_and_politics/explainer/2009/10/bootleg_nation.html.
- Chen, E., Orth, D. (2013). The strategy for digital citizenship. NAIS Independent School Magazine (online) http://www.nais.org/Magazines-Newsletters/ISMagazine/Pages/The-Strategy-for-Digital-Citizenship.aspx.
- Cofino, K. (2012, March 24). Digital citizenship: The forgotten fundamental. http://www.slideshare.net/mscofino/digital-citizenship-the-forgotten-fundamental.
- Common Sense Media (n.d.). Lesson in action: Super digital citizen. http://www.commonsensemedia.org/videos/lesson-in-action-super-digital-citizen
- Growth Coaching International (n.d.) Growth Framework [Image] https://www.growthcoaching.com.au/about/growth-approach?country=au
- Hague, C. and Payton, S. (2010). Digital Literacy Across the Curriculum (Futurelab Handbook). Futurelab. https://www.nfer.ac.uk/publications/FUTL06/FUTL06_home.cfm
- Hilt, L. (2011, October 26). The Case for Cultivating Cultural Awareness. http://plpnetwork.com/2011/10/26/the-case-for-cultivating-cultural-awareness/
- James, C., & Jenkins, H. (2014). Disconnected: Youth, New Media, and the Ethics Gap. MIT Press.
- Levinson, M. (2010). From fear to Facebook: One school’s journey. International Society for Technology in Education.
- Lindsay, J. (2016). The global educator: Leveraging technology for collaborative learning and teaching. International Society for Technology in Education.
- Lindsay. J. (2016, July 19). How to encourage and model global citizenship in the classroom. Education Week http://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/global_learning/2016/07/how_to_encourage_and_model_global_citizenship_in_the_classroom.html
- Lindsay, J. (2014, March 7). Digital citizenship: A global perspective. http://www.slideshare.net/julielindsay/digital-citizenship-a-global-perspective-reduced-size-32020944
- Lindsay, J. (2015, January 8). Leadership for digital citizenship action. http://www.slideshare.net/julielindsay/leadership-for-digital-citizenship-action-acec-2015
- Michaelsen, A. (2013, October 10). Connected educators for connect learners #ce13. http://annmic.wordpress.com/2013/10/10/connected-educators-for-connect-learners-ce13/
- Mirtschin, A. (2012, January 18). Empowering digital citizenship action. http://murcha.wordpress.com/2012/01/18/empower-digital-citizenship-action/
- Mirtschin, A. (2015, November 4). Talk of the school! https://murcha.wordpress.com/2015/11/04/talk-of-the-school/
- Murray, T. (2013, January 7). 10 steps technology directors can take to stay relevant. http://smartblogs.com/education/2013/01/07/the-obsolete-technology-director-murray-thomas/.
- Nielsen, L. (2012, October 29). 4 things you need to know to help your students manage their online reputation by. http://theinnovativeeducator.blogspot.co.uk/2012/10/4-things-you-need-to-know-to-help-your.html.
- Ohler, J. (2011). Character education for the digital age. ASCD Educational Leadership. 68(5). http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational-leadership/feb11/vol68/num05/Character-Education-for-the-Digital-Age.aspx.
- Oxley, K. (2012, August 12). Developing a digital citizenship program. http://www.slideshare.net/cathryno/developing-a-digital-citizenship-program.
- Pashiardis, P. (1996). Environmental scanning in educational organizations: uses, approaches, sources and methodologies. International Journal of Educational Management, 10(3), 5-9.
- Ribble, M.(2011). Digital citizenship in schools. International Society for Technology in Education.
- Sheninger, E. (2017, August 29). 7 pillars of digital leadership in education. https://www.teachthought.com/the-future-of-learning/7-pillars-digital-leadership-education/
- TeachThought Staff (2018, November 18). Moving students from digital citizenship to digital leadership. https://www.teachthought.com/the-future-of-learning/moving-students-from-digital-citizenship-to-digital-leadership/
- Tiven, M. E., Fuchs, E., Bazari, A., & MacQuarrie, A. (2018). Evaluating global digital education: Student outcomes framework. New York, NY: Bloomberg Philanthropies and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Digital Citizenship in the Curriculum (ETL523 Module 1)

21st Century learning and COVID-19 – catalysts for change:
 With the COVID-19 lockdown, the Digital Learning Environment (DLE) issues are relevant like never before. Teachers who have been allowed to stick to their paper programs, regurgitating content from previous classes that they’ve taught or from purchased sources and shying away from digital tools and applications, must now think on their feet to create online programs to suit their classes and individual students.
With the COVID-19 lockdown, the Digital Learning Environment (DLE) issues are relevant like never before. Teachers who have been allowed to stick to their paper programs, regurgitating content from previous classes that they’ve taught or from purchased sources and shying away from digital tools and applications, must now think on their feet to create online programs to suit their classes and individual students.
The Digital Education Advisory Group, approximately 8 years ago, wrote: “What is now required is a catalyst intervention to bring into recognisable focus the change that the whole community will recognise and welcome as transformation that shapes our future” …”We need to harness the transformative potential of digital technology to support new approaches to innovative learning centred around the development of 21st Century Learning skills. These include creativity and innovation; critical thinking, problem solving, decision making; life-long learning; collaboration and communication; ICT literacy; consciousness of being a local and global citizen; and personal and social responsibility” (Digital Education Advisory Group – DEAG, no date).
“Assuming a world in which the welfare of the young people and the economic health of a society and the political health of a democracy are the true goals of education, I believe modern societies need to assess and evaluate what works and what doesn’t in terms of engaging students in learning. If we want to do this, if we want to discover how we can engage students as well as ourselves in the 21st century, we must move beyond skills and technologies. We must explore also the interconnected social media literacies of attention, participation, cooperation, network awareness, and critical consumption” (Rheingold, 2010 p.24; emphasis added).
“Schools need not only to prepare students to be responsible citizens, but also to prepare them with the technological and communicative skills necessary to engage civic responsibility in a digital age” (Richards, 2010, p.520).
Teacher ability:
It takes a village: I wholeheartedly subscribe to the notion presented by Hollandsworth, Dowdy, & Donovan, (2011) that educators have a duty of care for student safety and security, educational enhancement, ethical and legal behaviours and becoming an effective member of communities, in both the physical and digital environment through policy, leadership and practice.
It does, indeed, ‘take a village to raise a child’ to be a good global and digital citizen, and this process should include all stakeholders: parents, teachers, teacher librarians, administrators, academics, technology professionals and, none the least of which, students. This means that educators must be proactive in effective digital citizenship DLE (including risk awareness et al), as well as in fostering student peer mentor programs, effective student role models, and quality educational faculty/staff DLE ability.
PLC, PLN, PLE, DLE: Furthermore, we as educators need to foster professional learning communities (PLC) through culture of personal learning networks (PLN) and personal learning environments (PLE), including networks within the Digital Learning Environment (DLE) according to ‘Steve Wheeler on future learning environments: professional, powerful and personal’ (YouTube / 2:09 mins) | https://youtu.be/db9PXLqoduQ
Creation of content:
There are some great resources for creating content, as recommended by ETL523 Module 1, including:
- https://www.commonsense.org/education/
- https://globaldigitalcitizen.org/
- http://www.newmedialiteracies.org/our-space-being-a-responsible-citizen-of-the-digital-world/
Just as most schools have created a school ‘code of conduct’, so too should they proactively (rather than reactively) teach a DLE ‘code of conduct’ (Hollandsworth, et al, 2011). And just as we review and evaluate the quality of our lesson content and physical curriculum, so too should educators have a structured means in which to create, deliver and then evaluate their online DLE digital citizenship curriculum. (I like the ‘writing on the bathroom wall’ analogy, which links toilet graffiti to the banter and issues that sometimes arise in social media platforms or chats-we should have a plan for how to help students handle these situations in both environments as neither are able to be fully policed or ‘filtered’ by adults). A great source of raising awareness in students are the Pause and Think by Commonsense Education.
In terms of ways to teach digital footprint ideas to students, I particularly like the videos by Everyone – Think before you post, and the blog post by Nielsen (2011), Discover what your digital footprint says about you.
Furthermore, we need to reconsider the curriculum and how we have created and delivered content in the past: “For educators and the schools in which they teach, the challenges of this moment are significant. Our ability to learn whatever we want, whenever we want, from whomever we want is rendering the linear, age-grouped, teacher-guided curriculum less and less relevant.” (Richardson, 2008, Emphasis added).
Brown, Dehoney and Milichap (2015) surmise that the core dimensions of Next Generation Digital Learning Environment (NGDLE) are:
- Interoperability and integration
- Personalisation
- Analytics, advising and learning assessment
- Collaboration
- Accessibility and universal design
Lindsay & Davis’ (2012) ‘enlightened digital citizenship model’ recommends we consider digital citizenship in terms of four areas of content:
- Safety and privacy
- Etiquette and respect
- Learning habits – workflow
- Literacy and fluency
Social media / Digital footprints (safety / privacy / brand):
We all have a digital footprint and we must model and teach an awareness of this to students. I agree with Richards (2010) who points out that we either teach students how to engage in social media responsibly, or risk them attempting it on their own, which is very much in line with research on sexual reproduction education. Wheeler equates learning about the internet to learning how to cross the road safely – what better place to teach these concepts than in school? (Wheeler, 2015, p.176).
I think it is imperative that this education begins prior to students having a substantial digital footprint, adhering to guidelines like ‘no facebook until you are 13’ – because teaching them to be mindful of what they display digitally after they have already begun displaying themselves, is like trying to teach someone who has just voted in a political election, how to vote. We must teach them early on how our digital footprint or identity is now our (online) personal ‘brand.’
We are identified at home in one way, at work or school in one way, and online or digitally in one way and our identities change through the passage of time. People can forget or not know anything about your identity in the real world, but in the digital environment, your identity is more permanent. Furthermore, the 21st century boundaries between these contexts are now blurred. We need to ask our students and them how to recognise ‘what is your identity?’ across these three platforms and throughout time.
We must therefore consider that students (and teachers) need to be literate in (aka be able to have understanding access) social media, which requires: attention, participation (civil or otherwise), collaboration, network awareness and critical thought (or critical ‘consumption’) as according to Rheingold, H. (2010).
 Something else to consider is that we have an expectation that students will be capable of digital citizenship, when their understanding of citizenship overall is still developing, particularly at the K-6 level. We must be aware of the way that we have learnt citizenship in the face to face world and how 21st Century learners have not had the same face to face opportunities and foundations that we’ve had. They must learn citizenship face to face and digitally simultaneously…like learning two different languages at the same time! Furthermore, social networks and social media have played a significant part in changing citizenship and previous boundaries and accepted expectations for social behaviour. Some face to face social constructs (such as body language) are not relevant in the digital social environment and as a result, effective use of emoticons or gifs or memes have been created to fill the void.
Something else to consider is that we have an expectation that students will be capable of digital citizenship, when their understanding of citizenship overall is still developing, particularly at the K-6 level. We must be aware of the way that we have learnt citizenship in the face to face world and how 21st Century learners have not had the same face to face opportunities and foundations that we’ve had. They must learn citizenship face to face and digitally simultaneously…like learning two different languages at the same time! Furthermore, social networks and social media have played a significant part in changing citizenship and previous boundaries and accepted expectations for social behaviour. Some face to face social constructs (such as body language) are not relevant in the digital social environment and as a result, effective use of emoticons or gifs or memes have been created to fill the void.
Delivery of content:
In order to deliver the content or curriculum, the devices and tools chosen must be convenient, consistent, and allow for frequent access to digital devices (Mann, 1999; Kelley & Ringstaff, 2002; NCES, 1999; and Statham & Torrell, 1999, in Kemker, 2005).
Having access to physical technology (primarily due to SES) is not the only issue. As pointed out by Jenkins, Clinton, Purushotma, Robinson & Weigel (2006), teachers who wish to obtain full involvement of their students by creating a ‘participatory culture,’ must also make adjustments to their pedagogy based on:
- Individual student ability to participate in the DLE given their varied access to opportunities, experiences, skills and knowledge,
- The varied degrees of understanding media transparency (or lack thereof) around how media shape world views, or how to apply filters for the large number of ‘hits’ or ‘tweets’ or emails that one receives so as to not become overwhelmed,
- and the varied degrees of understanding, training or socialisation of digital citizenship or ethical expectations for global DLE success.
 (Note to self: The issue of access to the internet, devices, applications and digital or social media tools in terms of Socio Economic Status and individual choice was covered in ETL401 and ETL503 and in my blog posts for those courses).
(Note to self: The issue of access to the internet, devices, applications and digital or social media tools in terms of Socio Economic Status and individual choice was covered in ETL401 and ETL503 and in my blog posts for those courses).
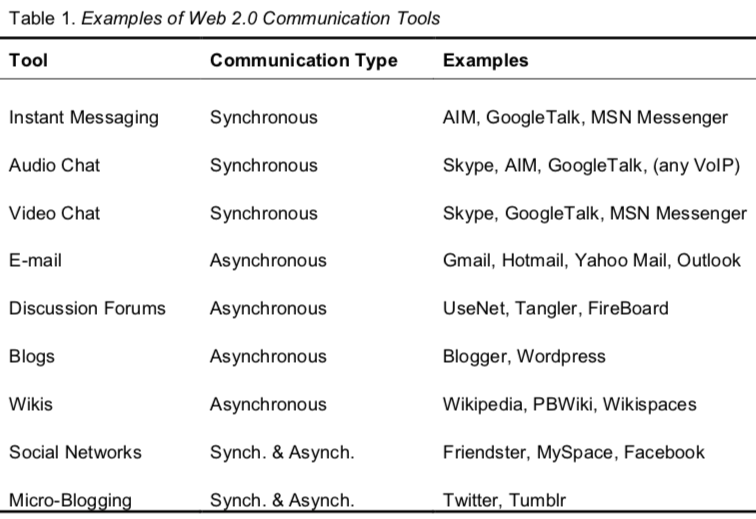
Furthermore, we must plan whether our delivery will be synchronous or asynchronous (or a mixture of the two): “Synchronous discussion is real-time or live communication that takes place on platforms such as instant messengers, audio chat, or video chat. Asynchronous discussion is non-live communication that takes place over time and includes platforms such as e-mail, discussion forums, blogs, and wikis” (Richards, 2010, p.516).
Evaluation & quality control:
Digital learning spaces need to be created in conjunction with digital citizenship awareness and incorporating essential attitudes and skills needed to be a productive (digital) learner . However, this means that digital citizenship is not just about recognising online copyright laws, or keeping students safe online. (See my previous post What is digital citizenship?).
Quality tools, lessons (either face to face or digitally) should enable students to be engaged in authentic tasks, connected to the real world, involving all partners of the learning community such as teachers, students, parents, business partners, and higher education experts (Kemeker, 2005). But, what can we use to measure student engagement and connectedness to ensure they are fully active, creative and ethical DLE participants?
Jenkins, et. al. (2006) have a comprehensive list of skills and competencies:

Prior to the DLE, quality standards, each with a scale of 1-5, were created by Newmann and Wehlage (1993) to help teachers assess the “authenticity” of classroom tasks and experiences, Newmann and Wehlage (1993): 1. Higher order thinking, 2. Depth of knowledge, 3. Connectedness to the world beyond the classroom, 4. Substantive conversation, and 5. Social support for student achievement – which is closely linked to the more expanded and also individually scaled from 1-5 Quality Teaching Framework (Gore, 2018):
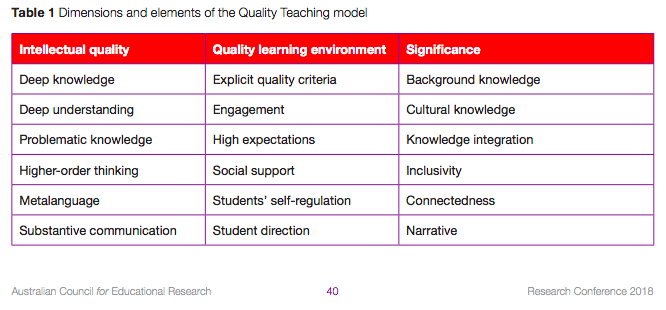

I think it is important to consider quality teaching and leadership standards within the context of the DLE, as well as the skills and competencies from Jenkins et al (2006) and possibly the 21st Century Learning skills identified from various sources (see previous blogs via tags).
References
Brown, M., Dehoney, J., & Millichap, N. (2015). The next generation digital learning environment. A Report on Research. ELI Paper. Louisville, CO: Educause April.
Digital Education Advisory Group. Beyond the classroom: A new digital education for Australian’s in the 21st Century. Retrieved from https://docs.education.gov.au/system/files/doc/other/deag_final_report.pdf
Gore, J. (2018). Dimensions and Elements of the Quality Teaching Model. [Image]. Australian Council for Educational Research – Research Conference 2018. Retrieved from https://research.acer.edu.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1336&context=research_conference
Hollandsworth, R., Dowdy, L., & Donovan, J. (2011). Digital citizenship in K-12: It takes a village. TechTrends, 55(4) 37-47.
Jenkins, H., Clinton, K., Purushotma, R., Robison, A. J., & Weigel, M. (2006). Confronting the challenges of participatory culture: Media education for the 21st century. MacArthur Foundation website https://www.macfound.org/media/article_pdfs/JENKINS_WHITE_PAPER.PDF
Kemker, K. (2005). The digital learning environment: What the research tells us. Apple White Paper. Retrieved from (see link).
Lindsay, J., & Davis, V. (2012). Flattening classrooms, engaging minds: Move to global collaboration one step at a time. Allyn and Bacon. Chapter 5: Citizenship. (available on CSU DOMS as a downloadable PDF)
Rheingold, H. (2010). Attention and other 21st century social media literacies. Educause Review 45(5). Retrieved from http://www.educause.edu/ero/article/attention-and-other-21st-century-social-media-literacies
Nielsen, L. (2011, August 19). Discover what your digital footprint says about you. Retrieved from http://theinnovativeeducator.blogspot.com/2011/08/discover-what-your-digital-footprint.html
Richards, R. (2010). Digital citizenship and Web 2.0 tools. Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 6(2), 516-522. Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/7740/fb40e7030935d7b00d5bd07a19ba83c496ff.pdf
Richardson, W. (2008, December 3). World without walls: Learning well with others. Edutopia. Retrieved from http://www.edutopia.org/collaboration-age-technology-will-richardson.
Wheeler, S. (2015). Learning with ‘e’s: Educational theory and practice in the digital age. Crown House Pub Ltd. Chapter 12: Literacy in a connected world.
Ideas for Developing a Future Ready Library in Pictures and Graphs

Leading Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
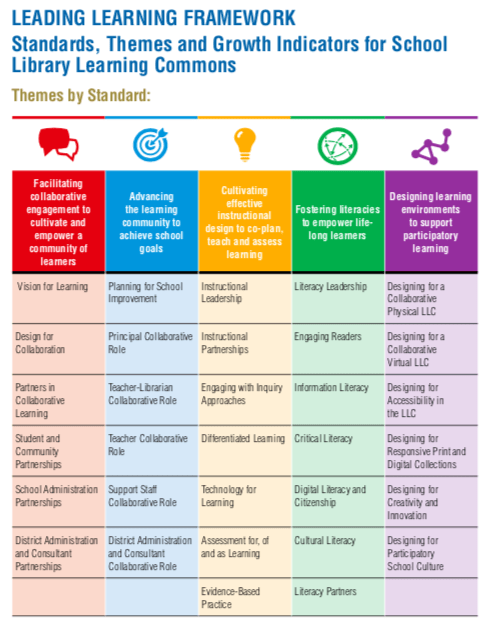
Leading Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
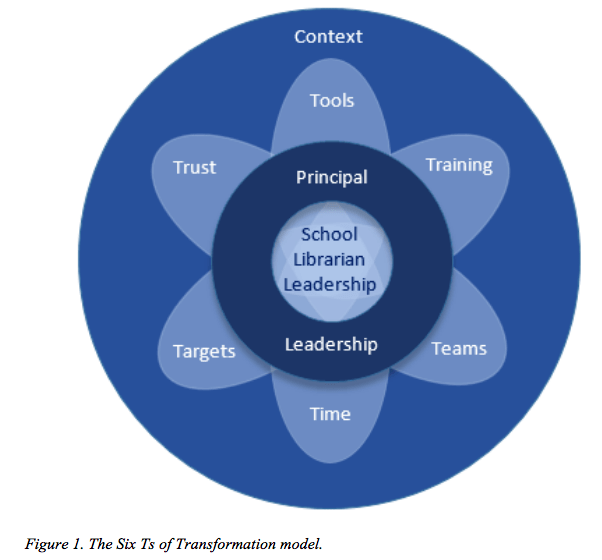

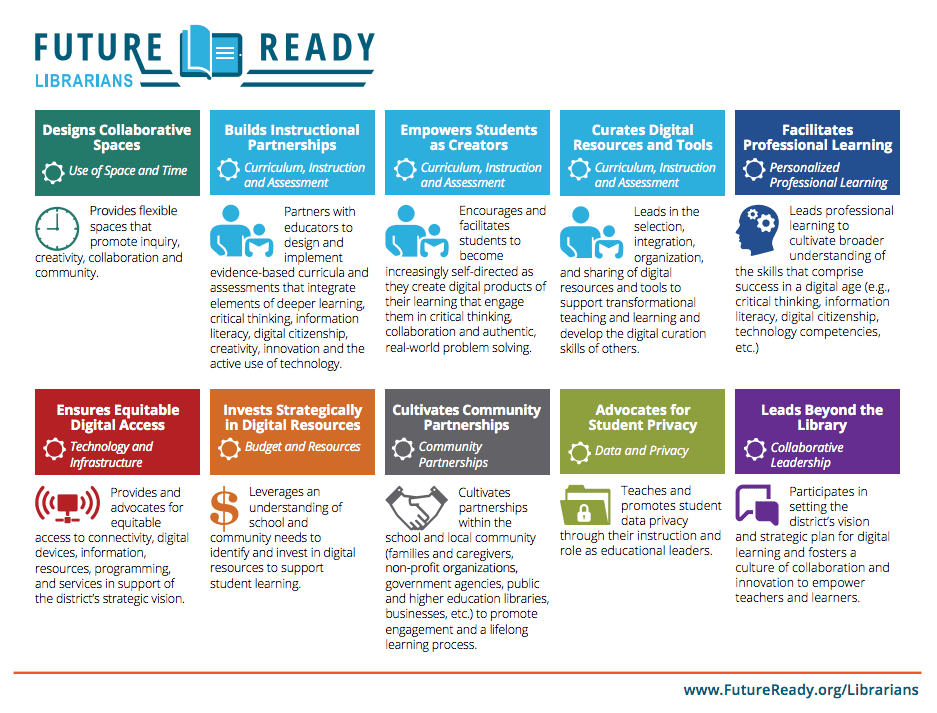
These images are great resources and worth remembering and utilising for developing a future ready school library ‘learning commons.’ Where are Australia’s ideas for future ready libraries? Are they just for members of ASLA only or is the ASLA ‘futures’ white paper the only resource we’ve yet to produce? Why are we relying on the resources from North America?
References
Alliance for Excellent Education (2016). Future ready librarians [Image]. In Future Ready Schools. Retrieved from http-/1gu04j2l2i9n1b0wor2zmgua.wpengine.netdna-cdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Library_flyer_download
Baker, S. (2016). Figure 1. The six Ts of transformation model. [Image]. In School libraries Worldwide, 22(1), 143-159. Retrieved from http://www.iasl-online.org/resources/Documents/PD%20Library/11bakerformattedfinalformatted143-158.pdf
Canadian Library Association. (2014). Leading Learning Framework – Standards, Themes and Growth Indicators for School Library Learning Commons. [Image]. In Leading Learning- Standards Of Practice For School Library Learning Commons In Canada. Ottawa, ON- Canadian Library Association. Retrieved from https://apsds.org/wp-content/uploads/Standards-of-Practice-for-SchoolLibrary-Learning-Commons-in-Canada-2014.pdf
Canadian Library Association. (2014). Key Steps for Implementation. [Image]. In Leading Learning- Standards Of Practice For School Library Learning Commons In Canada. Ottawa, ON- Canadian Library Association. Retrieved from http-//clatoolbox.ca/casl/slic/llsop.html
Future Ready Schools (2019). The 7 Gears [Image]. In The Future Ready Framework. Retrieved from https///dashboard.futurereadyschools.org/framework
Reflection on Module 3.3 Change Leader – SO MANY IDEAS!
“Change management is important but change leadership is essential” (Pennington, n.d.). Leadership versus Management:
Have a clear understanding about the difference between leadership and management, because if something turbulent happens that means an organisation or school is required to implement change and we are stuck in management tasks, we can’t lead (Kotter, 2013).
Therefore, leadership (leading) is: creating a strategy and vision for the future and creating an environment that motivates others to join the vision and strategy; whereas management (functional) is: planning, budgeting, organising, staffing controlling and problem solving (Kotter, 2013).
[I won’t write too much more about management versus leadership because I think I’ve written loads about this in my blog posts for ETL503 Resourcing the Curriculum]

Innovation versus change:
 I think we also need to have a clear definition as to what is innovation versus change. The two seem to be being used interchangeably in this course, and in some ways that could be dangerous, particularly given the ‘change fatigue’ discussed in my previous post(s). Innovation is change that is adding value for both the company and the customer [as detailed by Nick Skillcom from Idea to Value (2019)], but change doesn’t necessarily do this and promoting a ‘change culture’ frightens me. We need to remember to match innovation (and subsequent change) to goals. Perhaps a ‘change culture’ is an innovative culture that is open to change, but not necessarily constantly changing?
I think we also need to have a clear definition as to what is innovation versus change. The two seem to be being used interchangeably in this course, and in some ways that could be dangerous, particularly given the ‘change fatigue’ discussed in my previous post(s). Innovation is change that is adding value for both the company and the customer [as detailed by Nick Skillcom from Idea to Value (2019)], but change doesn’t necessarily do this and promoting a ‘change culture’ frightens me. We need to remember to match innovation (and subsequent change) to goals. Perhaps a ‘change culture’ is an innovative culture that is open to change, but not necessarily constantly changing?

These are interesting, given the wording of the principal standards from the Australian Institute for Teaching and School Leadership (AITSL): “Identify the need for innovation and improvement; Develop a process and common language for change; Maintain their values whilst adapting flexibly and strategically to changes in the environment; Embed a culture of continuous improvement (AITSL, 2015).
Innovation: In order to recognise necessary innovations, I need to identify my passion. What’s my passion? Literacy. Quality literature. Education of children. Helping others find their passion. Encouraging colleagues to promote the social and emotional learning of students.
Professional Goals: 1. linking my practices to research; 2. linking my practices to the ASLA librarian standards.

Leading from the middle:
The whole premise behind this is to build capacity in others, which is what we do as teachers every day (Gottlieb, 2012). First we must lead by doing, and must get to know our team at a personal level. Gottlieb (2012) has many ideas about how to run a meeting or series of meetings to achieve this.
 Morning meetings that build personal connections link to the teacher/students’ ‘morning meeting’ idea in the new wave of positive behaviour for learning and trauma informed practice pedagogy promoted by the Berry Street Educational Model (BSEM) or the Responsive Classroom.
Morning meetings that build personal connections link to the teacher/students’ ‘morning meeting’ idea in the new wave of positive behaviour for learning and trauma informed practice pedagogy promoted by the Berry Street Educational Model (BSEM) or the Responsive Classroom.
Gottlieb (2012) also suggest we create a website page of our team ‘biographies’ to help team members get to know each other and reinforce such things as: What are your values or strengths? What excites you about our strategic plan or mission? Why are the things we do in our library important? What is your personal journey that has brought you here, or what is your personal teaching and learning philosophy?
 Well hell’s bells, I thought of this ‘Spotlight’ idea too about two years ago and my supervisor at the time thought it was a great idea! Unfortunately, his son fell ill and he had to move away before the idea came to fruition (and his replacement did not renew my contract). Time to dust off the idea and utilise it in my future library!
Well hell’s bells, I thought of this ‘Spotlight’ idea too about two years ago and my supervisor at the time thought it was a great idea! Unfortunately, his son fell ill and he had to move away before the idea came to fruition (and his replacement did not renew my contract). Time to dust off the idea and utilise it in my future library!
Implementing an innovation culture (not a change culture!):

Opinion based on my own experience: Changing the work culture in a school is a really big deal. Some might even say, insurmountable. When inundated with ‘top down’ policies, budget constraints, and a ‘to be run like a business’ mantra (influenced by a employment policy for administration staff that literally advocates for nepotism; ‘local schools local decisions;’ promotion on ‘merit’ being rorted – particularly for leadership positions; the bullying of bureaucrats and top-level executives resulting in the bullying of leaders; resulting in bullying of teachers, resulting in bullying of students, resulting in bullying on the playground; the oversupply of teachers (particularly new scheme teachers) in primary and the undersupply in secondary; the push to employ more (new scheme) temporary contract teachers (who struggle with building relationships with students – one of the main indicators of academic success) in primary over offering permanent positions – pitting the temps’ against each other in competition for the few permanent positions that arise; laying off temps in favour of ‘free trial’ teachers in from the city on incentive schemes, etc) trying to change a school culture from the bottom up, (or ‘the middle’ as per Gottlieb, 2012) at this stage is all but futile.
And while I agree that we need to develop as teachers, I am struck by Lortie’s (1975 in Oberg, 2011) terms “presentism, conservatism; and individualism” as being hinders to the change process. When I read this, I saw it as the bureaucratic level trends in society and global political trends rather than or in addition to the trends in teacher attitudes towards ‘change’ / innovation.
A Google dictionary search defines the terms as: “Presentism: uncritical adherence to present-day attitudes, especially the tendency to interpret past events in terms of modern values and concepts.”…”Conservatism: commitment to traditional values and ideas with opposition to change or innovation; (or) the holding of political views that favour free enterprise, private ownership, and socially conservative ideas.”…”Individualism: the habit or principle of being independent and self-reliant; (or) a social theory favouring freedom of action for individuals over collective or state control.”
Wealth doesn’t ‘trickle down,’ but leadership attitudes seem to, as supported by Harvard Business Review (Zenger & Folkman, 2016).
The trick is to try to stop the ‘trickle down’ effect from reaching the students – and in that, the buck stops with me! I’m reminded of the social emotional lesson (learned from BSEM trauma informed practice teacher training) that I teach to students about things they can control. (I can’t control the bureaucrats or political arena, but I can control myself!)
 Thus, to combat anti-innovative mindsets, I will aim to address my personal presentism, conservatism and individualism mindset(s) through: professional development, personal reflection, collaboration, questioning the validity of top-down changes (such as data collection, standardised testing, and mandatory curriculum), as well as battling the conservative practices of social inequity and lack of cohesion that trickle down to school inequities–further disadvantaging marginalised students (Oberg, 2011).
Thus, to combat anti-innovative mindsets, I will aim to address my personal presentism, conservatism and individualism mindset(s) through: professional development, personal reflection, collaboration, questioning the validity of top-down changes (such as data collection, standardised testing, and mandatory curriculum), as well as battling the conservative practices of social inequity and lack of cohesion that trickle down to school inequities–further disadvantaging marginalised students (Oberg, 2011).
 Regarding ‘top down’ changes and conservative practices: I will confidently ask my team(s) the question: ‘How can this innovation (such as a behaviour peg chart or stoplight ‘welfare’ policy), which is intended to improve teaching and learning, contribute to making a difference for all stakeholders and all students, or will it make a difference only for those already advantaged (such as those who are meeting outcomes, have social capital, or who come from economically stable, privileged backgrounds)?’ (Oberg, 2011 p.2).
Regarding ‘top down’ changes and conservative practices: I will confidently ask my team(s) the question: ‘How can this innovation (such as a behaviour peg chart or stoplight ‘welfare’ policy), which is intended to improve teaching and learning, contribute to making a difference for all stakeholders and all students, or will it make a difference only for those already advantaged (such as those who are meeting outcomes, have social capital, or who come from economically stable, privileged backgrounds)?’ (Oberg, 2011 p.2).
 I will get to know the teaching and learning philosophies influencing teaching practices, the school’s attitudes towards innovation (or if it is simply ‘change’), how the teachers interact (in isolation or collaboratively), the executive team roles and goals, and the methods for determining success – both professionally and academically (Pratt, 2017; Oberg, 2011, p.2; Green 2011).
I will get to know the teaching and learning philosophies influencing teaching practices, the school’s attitudes towards innovation (or if it is simply ‘change’), how the teachers interact (in isolation or collaboratively), the executive team roles and goals, and the methods for determining success – both professionally and academically (Pratt, 2017; Oberg, 2011, p.2; Green 2011).
 I will proactively start in ‘my’ library by being patient with the innovation process (Pratt, 2017; Oberg, 2011), working flexibly and collaboratively with all stakeholders, setting SMART goals that are based on both the school mission/strategic plan/library mission/strategic plan of improving teaching and learning as well as based on evidence/research based innovations of 21st century teaching practices such as differentiation (Oberg, 2011; Green 2011).
I will proactively start in ‘my’ library by being patient with the innovation process (Pratt, 2017; Oberg, 2011), working flexibly and collaboratively with all stakeholders, setting SMART goals that are based on both the school mission/strategic plan/library mission/strategic plan of improving teaching and learning as well as based on evidence/research based innovations of 21st century teaching practices such as differentiation (Oberg, 2011; Green 2011).
Things I currently lack but need in a future teacher librarian role (according to Green (2011, p.23)): “established authoritative position, credibility amongst peers, a vision that is based on best practice and, importantly, a mandate to implement or produce change (innovation).”
 I need to utilise my skills in linking practice to researched evidence, marketing, ICT and QTR (as well as from training and experience received from BSEM, L3, AL and TEN, etc) in my library and collaborate with teachers, offering professional development in these areas, in order to help them utilise evidence-based practices, helpful computer technologies, effective lesson structures or to professionally and collaboratively evaluate their lessons or units of work (Green 2011).
I need to utilise my skills in linking practice to researched evidence, marketing, ICT and QTR (as well as from training and experience received from BSEM, L3, AL and TEN, etc) in my library and collaborate with teachers, offering professional development in these areas, in order to help them utilise evidence-based practices, helpful computer technologies, effective lesson structures or to professionally and collaboratively evaluate their lessons or units of work (Green 2011).
References
Australian Institute for Teaching and School Leadership (AITSL). (2015). Interactive leadership profiles. In AITSL.Retrieved from https://legacy.aitsl.edu.au/leadership-profiles/interactive-profiles/leading-improvement-innovation-and-change
Gottlieb, H. (2012, October 30). Leading from the middle: Bringing out the best in everyone [Blog post]. Retrieved from https://creatingthefuture.org/leading-from-the-middle-bringing-out-the-best-in-everyone/
Green, G. (2011). Learning leadership through the school library. Access, 25(4), 22-26. Retrieved from http://www.asla.org.au/publications/access.aspx
Kotter, J. (2013, August 15). The key differences between leading and managing [Video file]. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SEfgCqnMl5E [4.23 mins].
Oberg, D. (2011). Teacher librarians as cultural change agents. SCIS Connections, 79. Retrieved from https://www.scisdata.com/media/1353/connections-79.pdf
Pennington, R. (n.d.). How to make change work. In Educational leaders: Leading and managing change. Retrieved from http://www.educationalleaders.govt.nz/Leading-change/Leading-and-managing-change
Pratt, A. (2017). The challenge of implementing change. SCIS Connections, 103. Retrieved from https://www.scisdata.com/connections/issue-103/the-challenge-of-implementing-change
Skillcom, N. (2019). What is innovation? 15 experts share their innovation definition. Retrieved from https://www.ideatovalue.com/inno/nickskillicorn/2016/03/innovation-15-experts-share-innovation-definition/
Zenger, J. & Folkman, J. (2016). The trickle down effect of good and bad leadership. Harvard Business Review. Retrieved from https://hbr.org/2016/01/the-trickle-down-effect-of-good-and-bad-leadership
Information Literacy and Inquiry Based Teaching
I enjoyed the CRAAP test video , CRAAP rubric and Get REAL rubric, and I was searching for information seeking processes and look what I found! A BS-O-Meter! I can’t remember what forum discussion I was in that mentioned we needed one of these, but voila! Here it is! (I will put it into the forum discussions later):
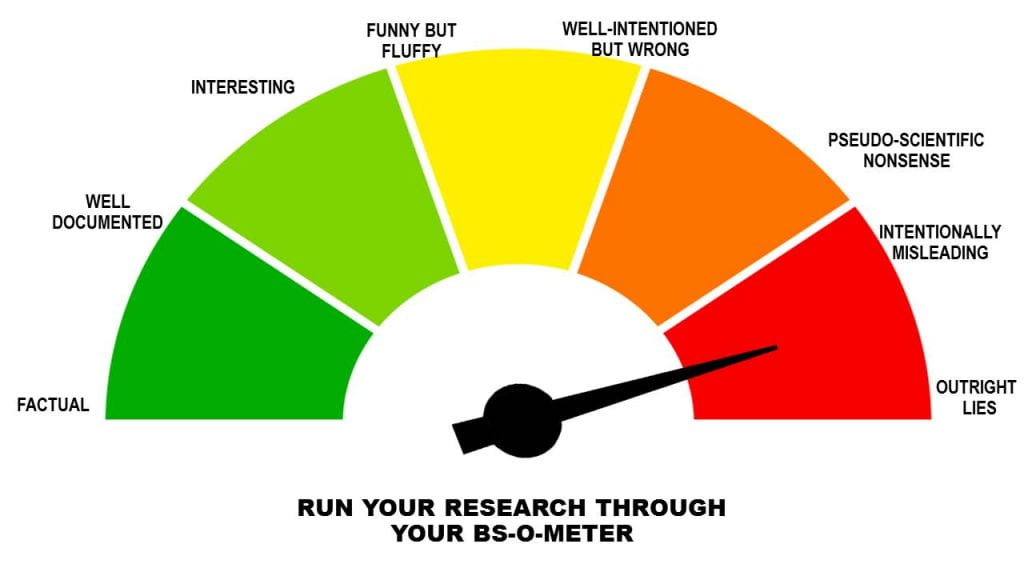
These devices help us teach the digital literacy aspect of information literacy. What is information literacy? I have grown to understand it better and better and particularly found this quote to be important:
“Understanding information literacy as a catalyst for learning necessitates a move away from exploring textual practices towards incorporating an understanding of the sociocultural and corporeal practices that are involved in coming to know an information environment” (Loyd 2007, pp. Abstract).
Information Literacy is but one form of the the vast aspects of literacy, sometimes referred to as multi-literacies, multi-modal pedagogy or trans-literacy. And basically what it boils down to is that, because of the multiplicity of literacy, educators (including TLs!) need a “pedagogical repertoire” in order to teach all aspects and forms of literacy (Kalantzis & Cope 2015).
I am heartened by the American Library Association (2016): “Information literacy forms the basis for lifelong learning. It is common to all disciplines, to all learning environments, and to all levels of education. It enables learners to master content and extend their investigations, become more self-directed, and assume greater control over their own learning. … …Information literacy, while showing significant overlap with information technology (digital literacy) skills, is a distinct and broader area of competence.”
According to the ALA, (2016) we must help our students become information literate individuals who can:
-
- “determine the extent of information needed;
- access the needed information effectively and efficiently;
- evaluate information and its sources critically;
- incorporate selected information into one’s knowledge base;
- use information effectively to accomplish a specific purpose; and
- understand the economic, legal, and social issues surrounding the use of information, and access and use information ethically and legally” (ALA 2016).
In the Teacher Librarian field, inquiry teaching models have been identified as the best means for enabling information literacy in students.
Maniotes and Kahlthau (2014) explain that inquiry teaching models support the information literacy (and research) for all ages because it is learning centred and focuses on emotionally stimulating questioning and deep understanding rather than product-driven answering and fact finding.
The inquiry teaching model is not presently taught very often or with rigour in most educational settings and this is where, according to Maniotes and Kahlthau (2014), the TL is vital!
In the upper years (age 9 and above) the use of Guided Inquiry Design (GID) is one of the models that is popular. Maniotes and Kahlthau describe it as a framework of inquiry learning design, as represented in 8 sequential phases “Open, Immerse, Explore, Identify, Gather, Create, Share, and Evaluate” (Maniotes & Kahlthau 2014, pp.Abstract).
As I teach the younger years predominantly, I have chosen to work with the Super3 and Big6 Inquiry teaching models and I am hopeful that I can do the pedagogy justice. I am certainly going to give it my best shot!
References
ALA (2016). Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher education. Retrieved from: https://alair.ala.org/handle/11213/7668
Lloyd, A. (2007). Recasting information literacy as sociocultural practice: Implications for library and information science researchers. Information Research, 12(4).
Kalantzis, M. & Cope, B. (2015). Multiliteracies: Expanding the scope of literacy pedagogy. New Learning.
Lloyd, A. (2007). Recasting information literacy as sociocultural practice: Implications for library and information science researchers. Information Research, 12(4).
Maniotes, L. K., & Kuhlthau, C. C. (2014). MAKING THE SHIFT. Knowledge Quest, 43(2), 8-17. Retrieved from https://search-proquest-com.ezproxy.csu.edu.au/docview/1620878836?accountid=10344
Young, L. (2019). BS-O-Meter. [Image]. Retrieved from: https://libguides.furman.edu/medialiteracy/framework
The New Paradigm Part 2 of 2
[ETL401 Module 4]
The New Paradigm: Let’s do both inquiry based learning and outcomes
In the previous post, I discussed collaboration and the steps that I think might be needed to get to a point where I can collaborate with the majority of teachers.
I’ve looked at the research and looked at the *information literacy inquiry models (particularly those more suited to primary and infants classes, such as Big6 and Super3) and okay, I’m in. Where do I sign?
*References in support of Inquiry based teaching and learning:
Bonanno, K. (2015). F-10 Inquiry skills scope and sequence and F-10 core skills and tools. Eduwebinar Pty Ltd, Zillmere, Queensland. Retrieved from: https://s2.amazonaws.com/scope-sequence/Bonanno-curriculum_mapping_v1.pdf
FitzGerald, L (2015) Guided Inquiry in practice, Scan 34/4,16-27
Kuhlthau, C., Maniotes, L. & Caspari, A. (2015) GI: Learning in the 21st century, 2nd edition. Santa Barbara, California: Libraries Unlimited.
Global Education Leadership Programme (GELP, 2011). We wanted to talk about 21st Century education. Retrieved from:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nA1Aqp0sPQo
O’Connell, J. (2012). So you think they can learn? Scan, 31, May, 5-11
The New Paradigm Part 1 of 2
(Reflection ETL401 Module 4 – The Teacher Librarian and the Curriculum)
(RSA Animate 2008) This is a very powerful video that offers a dichotomous view of an ‘education paradigm’.
Throwing the baby out with the bath water: While I agree that there has been (or in some cases, needs to be) a shift in the Australian education system, I am hesitant to throw out the baby with the bath water and dispose of outcomes. I have had great success with my students by utilising the NSW syllabus document outcomes and indicators. These have been regularly updated and rearranged over the years and each update, in my opinion, has improved the approach.
Similarly, so have approaches such as ‘play based learning’ or the ‘Reggio Emilia Approach’ / the environment as the ‘third teacher’ (Wein 2015), integrated units such as COGS and inquiry based learning (IBL) such as The Big6 or the Super3 / project based learning (PBL) models evolved over time and have been accepted and used by teachers to varying degrees and with varying degrees of success.
A Breath of Fresh Air: Anyone in the education system for more than 5 years will have seen enough new ideas blow in to the educational sphere to know that they generally blow straight back out to make room for the next big breeze, and leave very little in their wake in terms of real change.
I don’t think this ‘New Paradigm’ is a situation of ‘outcomes based learning’ vs ‘inquiry based  learning.’ I don’t think the two need to be pitted against each other in an argument reminiscent of the recent arguments about how to teach literacy as seen in media and other outlets, for example as per this 2017 blog post by Eleanor Heaton about phonics versus the whole language approach.
learning.’ I don’t think the two need to be pitted against each other in an argument reminiscent of the recent arguments about how to teach literacy as seen in media and other outlets, for example as per this 2017 blog post by Eleanor Heaton about phonics versus the whole language approach.
I see no reason why we can’t have both and simply be more flexible in the application of outcomes to meet real individual student needs.
The real issues with outcome based teaching are based in 1. a lack of authentic growth mindset (Dweck 2006) in adults and students – an inability to see mistakes as part of learning, 2. the social debate regarding reporting to parents and telling the students themselves or their parents that their child has or has not met stage outcomes based on a ‘letter’ mark or tick in a box. Far better, according to Hattie & Peddie (2003), for the system to simply say, ‘this is what sorts of things you/your child can do well, these are things that they are still learning or here are the learning goals for the future.’ It isn’t the outcomes at fault, it is how we’ve applied them to our practice as educators.
 [Sidebar 1: To this end, I am extremely interested in the Quality Teaching Framework to improve the structure of lesson delivery (if this is done through inquiry based teaching then so be it) and reading more about ability/interest/friendship grouping of students as opposed to age/year/stage grouping of students.]
[Sidebar 1: To this end, I am extremely interested in the Quality Teaching Framework to improve the structure of lesson delivery (if this is done through inquiry based teaching then so be it) and reading more about ability/interest/friendship grouping of students as opposed to age/year/stage grouping of students.]
[Sidebar 2: If you think Outcome based teaching is holding students back, don’t even get me started on the ‘Learning Progressions,’ ‘NAPLAN’ and the ‘Our Schools’ Website / league tables which have resulted in ‘teaching to the test’ and ‘school shopping.’ Gah.]
[Sidebar 3: If outcome models are so flawed and inquiry models are so perfect, why aren’t universities scrapping outcome based marking criteria and using inquiry models?]
Making assumptions about students: How students find information and their level of ability, particularly when it comes to electronic resources varies widely – much more so than adults realise and according to Coombes, “The basic premise of the Net Generation theory, that familiarity with technology equates with efficient and effective use and these achievements are only applicable to a specific group because they have grown up with technology, is flawed” (Coombes 2009, pp.32).
Technology is a tool, rather than a solution (Coombes 2009). Society has a new ‘digital age’ environment in which we live and we are expecting students to learn how to navigate it simply by being born amongst it. We have a new set of digital expectations in our society but have neglected to update our education system of our students to enable them to meet those expectations.
Information Search Process (ISP) skills / information literacy: Being able to recognise functions of a digital device does not automatically mean that students are able to access, process and absorb information on that they come across on said device (Coombes 2009). Students are overly reliant on the internet, have limited ability to search effectively, and are rarely able to critically evaluate information that they find (Coombes 2009).
The Role of Teacher Librarians (et al.): Educators have responsibility to lift their game when it comes to teaching students information literacy / searching skills such as collecting, managing and evaluating information (particularly when they believe the first thing that appears in their search is the most relevant or most accurate when in fact the first thing that comes up is based on their prior searches and the search engine’s popularity algorithms), finding the information again at a later date, and storing information for future use (Combes, 2007b in Coombes 2009).
Evidence and Assessment within the library: I like the list of ideas in ETL401 Module 3 (based on Valenza 2015) for evidence that the library program is of benefit to the school teaching and learning programs and curriculum. However, I am wary of introducing something that is trivial or that will not stand the test of time or that might sit in a filing cabinet – lost and forgotten.
For that reason, I will use the Quality Teaching Framework and the subsequent evaluation sheet (that I modified on GoogleDocs) to evaluate my lessons or units of work professionally, and will also use the (yet to be created) school library website or more private/access restricted photo/video-based programs (where accepted by the school) for evidence of student engagement or achievement such as ClassDojo, Seesaw or ClassCraft. The benefit of these applications is that they are also able to be used by students themselves, with any device (at home or at school).
I’m looking at you, teachers who profess to be techno-phobes! As Coombes’ 2009 work was written 10 years ago, and research within her article is based on the 10 to ‘teen’ age range, most of the students in her focus are now adults and quite possibly, teachers themselves. Those who are from current and previous generations, as educators, need to be aware of our own gaps in information literacy so that we can stop the cycle of poor information seeking skills!
The Blame Game: What I’ve also seen in education, in varying degrees based on context, is a lack of personal and professional reflection. A lack of ‘mindfulness’ and being in the moment. A wish for the utopian environment and an unrealistic desire for perfect students who fit into a mould and live up to unrealistic expectations and students who are compliant rather than collaborative (Goss & Sonnemann 2017).
This results in a filtering down of ‘blame’ for the poor foundational (primarily literacy and numeracy) skills that students have when they arrive into high school. The high school teachers blame the stage 3 teachers. The stage 3  teachers blame the stage 2 teachers. The stage 2 teachers blame the stage 1 teachers. The stage 1 teachers blame the kindergarten/prep teachers. The kindy/prep teachers blame the preschools. (And everybody blames the RFF teachers and the parents and finally, the students themselves).
teachers blame the stage 2 teachers. The stage 2 teachers blame the stage 1 teachers. The stage 1 teachers blame the kindergarten/prep teachers. The kindy/prep teachers blame the preschools. (And everybody blames the RFF teachers and the parents and finally, the students themselves).
What I’d like to see is every person involved in education taking a look in the mirror and reflecting daily on their pedagogical practice. What I’d like to see is everyone practising mindfulness–thoughtfully doing what they can with the students and contexts that they have in the moment in time in which they are living, and authentic growth mindset–appreciating that mistakes are part of learning.
References:
Combes, B. (2009). Generation Y: Are they really digital natives or more like digital refugees? Synergy, 7(1), 31-40
Dweck, C. (2016). What having a “growth mindset” actually means. Harvard Business Review, 13, 213-226.
Goss, P. & Sonnemann, J. (2017). Engaging Students – Creating classrooms that improve learning. Retrieved from: https://grattan.edu.au/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Engaging-students-creating-classrooms-that-improve-learning.pdf
Hattie, J., & Peddie, R. (2003). School reports: “Praising with faint damns.” Journal issue, 3.
RSA Animate – Robinson, K. (2008). Changing educational paradigms. Retrieved from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zDZFcDGpL4U#aid=P8wNMEma2ng
Valenza, J. (2015). Evolving with evidence: Leveraging new tools for EBP. Knowledge Quest. 43/3, 36-43
Wien, C. A. (2015). Emergent curriculum in the primary classroom: Interpreting the Reggio Emilia approach in schools. Teachers College Press.
Creating a Collaborative Climate – The Triple C’s
[Reflection of ETL401 & ETL503 (The TL Role in Collaboration)] (*addendum 16 September 2019 for ETL504)
 I think I’ve been pretty clear in my stance on the impact of temporary and casual work environments to the collaborative climate. If not, then I suppose I should mention here how much it wears away at collaboration to have individuals fighting for the renewals of their contracts: completely and utterly.
I think I’ve been pretty clear in my stance on the impact of temporary and casual work environments to the collaborative climate. If not, then I suppose I should mention here how much it wears away at collaboration to have individuals fighting for the renewals of their contracts: completely and utterly.
The casualisation of the teaching workforce, particularly in my personal working context, is not something I am able to change as an individual. Helping create a collaborative climate (despite the political climate) however, I can try to change.
Before we jump head first into collaborating with classroom teachers on an inquiry unit of work, let’s take a step back. I mean, yes we want to design and implement inquiry learning and literature programs and we certainly want to help embed digital formats. But we need to confront the elephant in the room in stead of simply shrugging our shoulders and saying ‘some teachers just don’t want to collaborate.’
I would argue that some teachers haven’t had positive collaborative experiences in the past (experiencing – much like a lot of students must experience – forced compliance rather than collaboration) or some teachers expect judgement in disguise rather than collaboration.
We ran into this in a school where we were trying to roll out Quality Teaching Rounds (QTR). We surveyed the staff to identify their concerns and these were the results:
Q. Why do we have to? (Comfort Zones: Not comfortable being watched / observed / critiqued; Doubt ‘teamwork’ capabilities; Criteria for involvement unclear; Feel pressured to do it).
A. (summarised) Be the change you wish to see in the world. Also, the NSW DET require a colleague observe you once a year so it might as well have a clear structure and limits and offer real improvement to your teaching.
Q. What’s the benefit? (Is there follow up; What do ‘we’ get out of it; Evidence of benefits; How does it improve the school; How valuable is it versus mentoring which we do already).
A. (shown QTR training slides proving benefits based on research)
Q. How could we possibly do it? (Logistics / Resources: What types of lessons have to be observed, eg 1:1, whole class, small group; Time off class; Casuals; Time required for prep work outside school hours).
A. (Thankfully, the principal had budgeted for the resources and did not have a set idea of what sort of lessons were required for observation).
The QTR team did our best with the resources and research provided by the QT Framework training to answer these concerns in a specially allocated staff meeting. We then surveyed the staff to determine their level of interest, which was about 70% in favour, and a few other teachers joined the second ‘Quality Teaching Round.’
Furthermore, in this process and in the readings for ETL401 Module 4, it occurred to me that an aspect of (primary) teaching that impacts collaboration is an ingrained and embedded culture of isolation. A teacher, predominantly alone in a room of students (or a Teacher Librarian on their own in the library) cannot effectively collaborate with other teachers as well as someone working in an office filled with cubicles or a group of engineers on a building site.
Another aspect of collaboration are the social norms of either Australian culture, or the culture of a town or city, or the culture of a school context. An immigrant and possible ASD person myself, I struggle with social norms on a daily basis.
I am also struck by the massive gap in the expectations of our TL role as collaborators, where we are expected to just jump in there and collaborate with teaching and learning programs with people who don’t know anything about us and of whom we also know very little…it is a bit ‘chicken before the egg’!
The OECD-UNICEF (2016) Education Working paper’s ‘dimensions of learning’ for organisation transformation touches on this (developing and sharing a student centred vision, having a culture of support for staff learning opportunities, promoting team collaborative professional development and embedding systems that support it, establishing daily expectations or ‘culture’ of inquiry, innovation and exploration–including staff in leadership roles, and learning with and from larger learning systems outside of the school context or direct governing body).
Logistically though, what does this look like? I love the idea of the ATSI community’s ‘yarning circle’. But how do I help create a ‘yarning circle’ or gathering spot where we can get to know each other and our contexts and socialise professionally? How do I help draw people out of their shells and into the safe environment of a collaborative climate?
Creating a Collaborative Climate (The triple C’s):
I can’t do it alone. There are things the executive must do to help improve the collaborative climate and things that they will need from me as well. However, once I’ve developed a rapport with the principal by helping them achieve their ideas, I will liaise with the principal to allow for time and budget amounts to be determined and allocated to enable some or all of the following of MY (8) ideas for creating a collaborative environment each year as follows:
- In an allocated staff meeting or staff development day, we sit in a ‘yarning circle’ and discuss ourselves, our school and any concerns openly and freely, using the ideas from this link as a guide: ATSI community’s ‘yarning circle’.
- Everyone completes the School Context Survey (draft version also in links on the right side of this blog) either collaboratively or on their own in time provided.
- Everyone takes the VIA Character Survey and shares their top 5 / 10 character traits for the year (they can change slightly each year).
- Everyone completes the Philosophy of Teaching Survey (draft version in links also on the right side of this blog). My own philosophy of Teaching has been updated for 2019 using the survey questions and can be used as a guide.
- A photo of the teacher is either created or supplied with their permission (see #7 below for format ideas) using the Photo Permission Form Template created by the American Library Association (or similar).
- The results of the school context, VIA, and philosophy surveys can then be sent electronically to the TL to be added to a electronic photo of the teacher(s) (with their permission), &/or collated and presented on an intranet or school website (which, unfortunately I do not have at present as I am not attached to a particular school).
- I even have ideas (I have a marketing background, don’t forget!) on what the end result would look like and have pinned these ideas onto my Teacher Spotlight Pinterest board. (This board could also, theoretically, be made available for all of the school staff to edit).
- And finally, (and this is where it gets a bit heavy), introduce Quality Teaching Rounds (in which I am an advocate and trained to deliver) to the school at least once a year if not twice, depending on budget and time allowances.
From here, collaborating on programming and teaching collaborative inquiry units are a walk in the park.
 *16 September 2019 ETL504 addendum: See the template link on the left of the blog for initiating a collaborative inquiry unit with a classroom teacher Created by Christy Roe, based on suggestions from Carr, J. (Ed.), (2008) p.13-14; 28; 39; and Bishop, (2011) p.7.
*16 September 2019 ETL504 addendum: See the template link on the left of the blog for initiating a collaborative inquiry unit with a classroom teacher Created by Christy Roe, based on suggestions from Carr, J. (Ed.), (2008) p.13-14; 28; 39; and Bishop, (2011) p.7.
WHEW! Its a big task. I hope I’m up to the challenge!
References:
Bishop, K. (2011). Connecting libraries with classrooms. Retrieved from ProQuest Ebook Central.
Carr, J. (Ed.). (2008). Leadership for excellence: Insights of the national school library media program of the year award winners. Retrieved from iG Library.
OECD-UNICEF. (2016). What makes a school a learning organisation? A guide for policy makers, school leaders and teachers. Retrieved from https://www.oecd.org/education/school/school-learning-organisation.pdf
![Hague, C., & Payton, S. (2010). Digital literacy across the curriculum [Handbook [Image]. pp. 19.](https://thinkspace.csu.edu.au/croe/files/2020/05/Hague-C.-Payton-S.-2010.-Digital-literacy-across-the-curriculum-Handbook-Image.-BECTA-FutureLab.-pp.-19.-National-Foundation-for-Educational-Research-httpswww.nfer_.ac_.uk-publicationsFUTL06FUTL06.pdf.png)

