Tag: Digital Citizenship
Best practice for leading and supporting digital citizenship
(Reflecting on my learning in ETL523 Modules 4, 5 & 6)
“Digital leaders understand that we must put real-world tools in the hands of students and allow them to create artefacts of learning that demonstrate conceptual mastery. This is an important pedagogical shift as it focuses on enhancing essential skill sets—communication, collaboration, creativity, media literacy, global connectedness, critical thinking, and problem solving – that society demands….Leaders need to be the catalysts for change…..Digital leadership begins with identifying obstacles to change and specific solutions to overcome them in order to transform schools in the digital age” (Sheninger, 2017).
Notably, in terms of creating a productive digital learning environment, Sheninger (2017) identifies ‘7 pillars for digital leadership in education’ as: communication, public relations, branding, student engagement/learning, professional growth/development, re-envisioning learning spaces and environments, and opportunity.
Rather than avoid global connections and social media, and rather than limit our students (forcing them to go ‘underground’ with a secret world of digital environments of their own making) we need need to learn how to embrace it safely and productively as global digital citizens (Ohler, 2011). We also need our school principals and supervisors to help promote a community of practice and positive learning environments by being “willing to listen, delegate, distribute, empower, and step out of the way of the learning” (Lindsay, 2016, p.110).
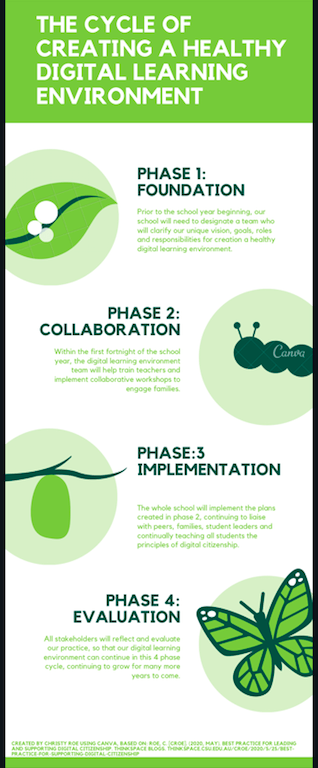
Utilising the readings for modules 4, 5 and 6, as well as a few of my own, following the 6 month multi-phase structure suggested by Chen & Orth (2013), Cofino (2012) and Common Sense Media (n.d.) which begins prior to the start of the school year, we can complete the following 4 phases:
-
Prior to the school year beginning, school contexts need to begin phase 1 by clarifying our unique vision, goals, roles and responsibilities:
- First. form a strong team of information and digital technology leaders (Chen & Orth, 2013; Common Sense Media, n.d.). (See my previous 9 blog posts on creating a school Community of Practice or the evaluation of practice via the 3 blog posts on Quality Teaching Framework/Rounds and also this video on Teacherpreneurs from the Centre for Teaching Quality for motivation!)
- Create and deliver an environmental scan utilising this template for a ‘Situational Analysis’ by Christy Roe (based on suggestions from) the resources provided by Hague & Payton (2010), and/or Pashiardis (1996), particularly as shown in the hexagon images below:
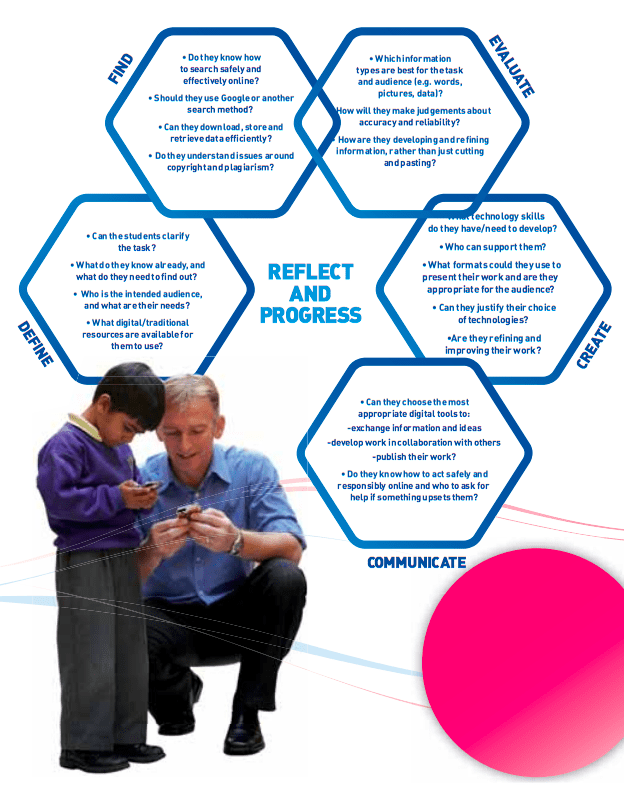
Digital Literacy Planning Tool ‘Reflect & Progress’ image by Hague & Payton, 2010, p.47 - Implement a technology audit (such as this one created by Christy Roe) and/or bullying survey (such as this one created by the University of South Australia) (Chen & Orth, 2013).
- Facilitate the formulation of policies, procedures or guidelines such as an acceptable use policy (using a questionnaire such as this one created by Christy Roe) based on the policy created by the administration (such as those listed in the resources section below), including cohesive terminology that we will utilise as a school (Common Sense Media, n.d.), e.g. linking the Positive Behaviour for Learning Behaviour Matrix or Code of Student Conduct to the school’s “Acceptable use Policy (AUP), Responsible Use Guidelines (RUG), Acceptable Use Agreement (AUA), Internet Use Policy (IUP), Bring Your Own Device (BYOD), or Bring Your Own Technology (BYOT)” etc.
- Liaise with others in our personal learning networks (PLN) (Sheninger, 2017) to map the digital citizenship areas of the syllabus or curriculum documents (NESA / ACARA), find examples of a digital citizenship scope and sequence (such as this (2011) one by Mike Ribble), develop sample lessons or units of work, and accumulate appropriate resources (such as those provided in the resources section below)–made available to all stakeholders (Common Sense Media, n.d.).
- Allow teacher librarians (and the school leadership teams) to readily undertake the role of information leaders who ‘meet the students where they are,’ recognising that there may not only be gaps in terms of technology access, or information access, but there may also be an (intergenerational) gap between what some view as the purpose of technology – i.e. is the purpose of technology to assist in informing, socialising or varying degrees of both, and what is true for the individuals in each school or home context? (Levinson, 2010, p.11).
2. In phase 2, within the first fortnight of the school year, we must train teachers and engage families:
“Alignment between school and home with regards to digital citizenship and healthy digital usage is a hallmark of a 21st-century school. A community-wide understanding of the norms, rules of behaviour, rules of engagement, and common practices is necessary for all schools in order to raise an ethical, digital (and real-life) citizen. Without this key parental partnership, these conversations regarding digital citizenship will just become incoherent whispers in the minds of our students, overwhelmed by the louder voices of media, false information, and misunderstanding” (Chen & Orth, 2013).
- As per the circles image from Hague & Payton (2010) (as well as information from Sheninger (2017)), schools and families need to continually foster 21st century learning and digital literacy skills such as: creativity, (innovation), critical thinking, evaluation (and problem solving), cultural and social understanding, collaboration, effective communication, (global collectedness), the ability to find and select information, (media literacy), e-safety and technological functional skills.
- While at the same time, we must also utilise situations of technology misuse as learning opportunities (see the POISE image below) for the students as well as ourselves as adult digital citizens, setting appropriate boundaries, listening student voices, and continuously encouraging digital literacy and digital citizenship (Chen & Orth, 2013).
- Educators as professionals need to get onboard with 21st century learning and nurture safe, culturally aware, global citizenship and global connections for ourselves as well as for and with our students (Hilt, 2011);
- We must ensure that our digital citizenship curriculum not only protects our students in terms of safety, privacy, copyright, fair use or legality issues, but that it also promotes global cultural, gender, socio-economic status, religion, language and ability awareness and a global appreciation of difference (Hilt, 2011).
- Educators who have embraced the need for global digital citizenship and global connections, need to lead by example and have our own safe, culturally aware, positive and professional ‘brand’ or digital footprint, and we also need to help our students create and tailor their own safe, culturally aware and positive digital footprint ‘brand(s)’ (Neilson, 2012).
- The digital citizenship leadership team, or perhaps even the whole staff, need to hold regular meetings and face to face information and collaboration sessions with families to ensure that preferred means of communication are clarified, that families have input into the digital citizenship program and also so that families are given support in implementing policies, procedures and guidelines at home that suit their individual situation(s) (Chen & Orth, 2013; Levinson, 2010).
- Finally, the digital citizenship team need to develop a plan to help students move from digital citizenship to digital leadership by creating a technology peer mentorship or student technology leadership program (such as YesK12.org) (Oxley, 2012; TeachThought Staff, 2018).
3. In phase 3, we must implement our plans:
- Prior to students being given devices, we must workshop the digital citizenship expectations, policy, procedures and guidelines that we created in phase 1 & 2 (Cofino, 2012).
“The message is threefold: (1) helping children become good digital citizens must be an ongoing practice led by families and schools together; (2) having access to a range of technology and global connections through school creates a positive context in which to have these conversations; and (3) students will make mistakes, and it’s our collective responsibility to turn mistakes into learnable moments” (Chen & Orth, 2013).
-

Bitmoji Christy ‘Do it!’ Once students begin to utilise digital devices, we must implement the digital citizenship lessons or units of work that we created in phase 2, with a key focus on 21st century learning skills, boundaries, student voice, digital footprints and global connections.
- We must implement the peer mentorship program that we created in phase 2, including student voice in the consequences for unacceptable behaviours (such as the student court, implied by in the slideshow by Cofino, 2012).
- We must continually check in with families, using the resources and communication devices agreed upon in phase 2.
4. And finally, in phase 4, we will reflect and evaluate:
![Growth Coaching International (n.d.) Growth Framework [Image]](https://thinkspace.csu.edu.au/croe/files/2020/05/Growth-Coaching-International-n.d.-GROWTH-Framework-Image.jpeg)
List of resources for Teachers and Students:
Policies, procedures or guidelines:
- New South Wales Department of Education and Training’s Policies & procedures > Student use of digital devices and online services (implemented January 27, 2020)
- eSafety Commissioner Teacher Resources;
- State of Victoria (Department of Education & Training) – Consent, Acceptable use agreements and Online services (updated November 2018)
- Sample BYOT Policies http://www.teachthought.com/technology/11-sample-education-byot-policies-to-help-you-create-your-own/
- Sample BYOD Policies http://www.k12blueprint.com/byod
- ‘An overview of school AUP’ written by David Warlick (2008)
- New Zealand Ministry of Education – Digital technology: Safe and responsible use in schools (2015). See also Netsafe.
- Code of Conduct (formerly Digital Citizenship Policy) Garibaldi Secondary School (USA).
- Using digital technologies to support learning and teaching – Victorian State Government, Australia
- Edutopia How to create social media guidelines for your school
- Alberta Canada Social Media Policy for School Districts
Resources for digital citizenship lessons:
- In addition to those recommended in my team’s ETL523 Assessment 2 website, there are also:

5 POISE Tips Infographic PDF by Christy Roe using information from Chen & Orth (2013) - 5 POISE Tips Infographic (shown here) by Christy Roe, based on information from Chen & Orth (2013) for use by both teachers and families
- Common Craft. (2011). Protecting reputations online. http://www.commoncraft.com/video/protecting-reputations-online.
- Common Sense Media. (2010, November 2). Our Connected Culture. http://youtu.be/L0XQj1anI-E
- eSafety Commissioner Cyberbullying resource
- Digital Life Student Intro Video by Common Sense Media, (2010),
- Overexposed
- Attention young professionals! What’s in your digital baggage?
- DontYouForgetAboutMe. (2007, August 11). Everyone – Think before you post (English). http://youtu.be/4w4_Hrwh2XI.
- ‘I Forgot My Phone’ (YouTube | 2:10 mins) | http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OINa46HeWg8 CharstarleneTV. (2013, August 22). I forgot my phone. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OINa46HeWg8.
Examples of global citizenship programs:
- Global Citizen Diploma program
- Lindsay, J. (2009, March 7). Digiteens go global. http://www.slideshare.net/julielindsay/digiteens-go-global (The Digiteens program is no longer running but information is still available about how to implement it).
- Mirtschin, A. (2012, April 26). Hello little world skypers. http://murcha.wordpress.com/2012/04/26/hello-little-world-skypers-group/
- Morgan, L. (2012, March 19). Skype with an astronaut! http://www.frugalteacher.com/2012/03/skyping-with-astronaut.html
- Internet censorship in China [Tag]. New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/search?query=internet%20censorship%20in%20china&sort=best
References and further reading
- Beam, C. (2011). Bootleg nation: How strict are Chinese copyright laws? Slate. http://www.slate.com/articles/news_and_politics/explainer/2009/10/bootleg_nation.html.
- Chen, E., Orth, D. (2013). The strategy for digital citizenship. NAIS Independent School Magazine (online) http://www.nais.org/Magazines-Newsletters/ISMagazine/Pages/The-Strategy-for-Digital-Citizenship.aspx.
- Cofino, K. (2012, March 24). Digital citizenship: The forgotten fundamental. http://www.slideshare.net/mscofino/digital-citizenship-the-forgotten-fundamental.
- Common Sense Media (n.d.). Lesson in action: Super digital citizen. http://www.commonsensemedia.org/videos/lesson-in-action-super-digital-citizen
- Growth Coaching International (n.d.) Growth Framework [Image] https://www.growthcoaching.com.au/about/growth-approach?country=au
- Hague, C. and Payton, S. (2010). Digital Literacy Across the Curriculum (Futurelab Handbook). Futurelab. https://www.nfer.ac.uk/publications/FUTL06/FUTL06_home.cfm
- Hilt, L. (2011, October 26). The Case for Cultivating Cultural Awareness. http://plpnetwork.com/2011/10/26/the-case-for-cultivating-cultural-awareness/
- James, C., & Jenkins, H. (2014). Disconnected: Youth, New Media, and the Ethics Gap. MIT Press.
- Levinson, M. (2010). From fear to Facebook: One school’s journey. International Society for Technology in Education.
- Lindsay, J. (2016). The global educator: Leveraging technology for collaborative learning and teaching. International Society for Technology in Education.
- Lindsay. J. (2016, July 19). How to encourage and model global citizenship in the classroom. Education Week http://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/global_learning/2016/07/how_to_encourage_and_model_global_citizenship_in_the_classroom.html
- Lindsay, J. (2014, March 7). Digital citizenship: A global perspective. http://www.slideshare.net/julielindsay/digital-citizenship-a-global-perspective-reduced-size-32020944
- Lindsay, J. (2015, January 8). Leadership for digital citizenship action. http://www.slideshare.net/julielindsay/leadership-for-digital-citizenship-action-acec-2015
- Michaelsen, A. (2013, October 10). Connected educators for connect learners #ce13. http://annmic.wordpress.com/2013/10/10/connected-educators-for-connect-learners-ce13/
- Mirtschin, A. (2012, January 18). Empowering digital citizenship action. http://murcha.wordpress.com/2012/01/18/empower-digital-citizenship-action/
- Mirtschin, A. (2015, November 4). Talk of the school! https://murcha.wordpress.com/2015/11/04/talk-of-the-school/
- Murray, T. (2013, January 7). 10 steps technology directors can take to stay relevant. http://smartblogs.com/education/2013/01/07/the-obsolete-technology-director-murray-thomas/.
- Nielsen, L. (2012, October 29). 4 things you need to know to help your students manage their online reputation by. http://theinnovativeeducator.blogspot.co.uk/2012/10/4-things-you-need-to-know-to-help-your.html.
- Ohler, J. (2011). Character education for the digital age. ASCD Educational Leadership. 68(5). http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational-leadership/feb11/vol68/num05/Character-Education-for-the-Digital-Age.aspx.
- Oxley, K. (2012, August 12). Developing a digital citizenship program. http://www.slideshare.net/cathryno/developing-a-digital-citizenship-program.
- Pashiardis, P. (1996). Environmental scanning in educational organizations: uses, approaches, sources and methodologies. International Journal of Educational Management, 10(3), 5-9.
- Ribble, M.(2011). Digital citizenship in schools. International Society for Technology in Education.
- Sheninger, E. (2017, August 29). 7 pillars of digital leadership in education. https://www.teachthought.com/the-future-of-learning/7-pillars-digital-leadership-education/
- TeachThought Staff (2018, November 18). Moving students from digital citizenship to digital leadership. https://www.teachthought.com/the-future-of-learning/moving-students-from-digital-citizenship-to-digital-leadership/
- Tiven, M. E., Fuchs, E., Bazari, A., & MacQuarrie, A. (2018). Evaluating global digital education: Student outcomes framework. New York, NY: Bloomberg Philanthropies and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development.
Protected: Critical Reflection for ETL523 Assessment 3 – What?, So what?, Now what?
How should educators design / develop / create / manage a digital learning environment (DLE)? (ETL523 Modules 3-5)

Why create a quality DLE?
The reasons behind and processes for creating a quality DLE is much like creating a ‘Learning Commons,’ (which I’ve discussed in two previous posts from ETL503 Resourcing the Curriculum: click here and here).
How do we create a quality DLE?
The article from Chen & Orth (2013) is absolutely amazing, not only because it points out that we must link the school DLE to the home DLE, but also because they outline the key steps to creating a quality DLE starting with 1. forming a group  of stakeholders, creating a shared vision and core beliefs, then 2. training, communicating with or informing all stakeholders, followed by 3. implementing the DLE plan of lessons and concepts of digital citizenship and digital literacy, completing the circle by 4. evaluating and reviewing the DLE regularly.
of stakeholders, creating a shared vision and core beliefs, then 2. training, communicating with or informing all stakeholders, followed by 3. implementing the DLE plan of lessons and concepts of digital citizenship and digital literacy, completing the circle by 4. evaluating and reviewing the DLE regularly.
How do we manage the DLE to foster globally connected learning?
As recommended by Lindsay (2016), we need to:
- Discuss the digital footprints or ‘branding’ of all students and make sure they are using long-term appropriate and culturally sensitive language and images.
- Consider the digital divide and make sure that platforms, discussion tools and global or local connections are provided synchronously (in real time) and asynchronously (offline or pre-recorded).
- Create a DLE that offers students opportunities to authentically and collaboratively engage with peers globally. (Lindsay, 2016).
How can we manage the DLE to move students from social media citizens to social media leaders?
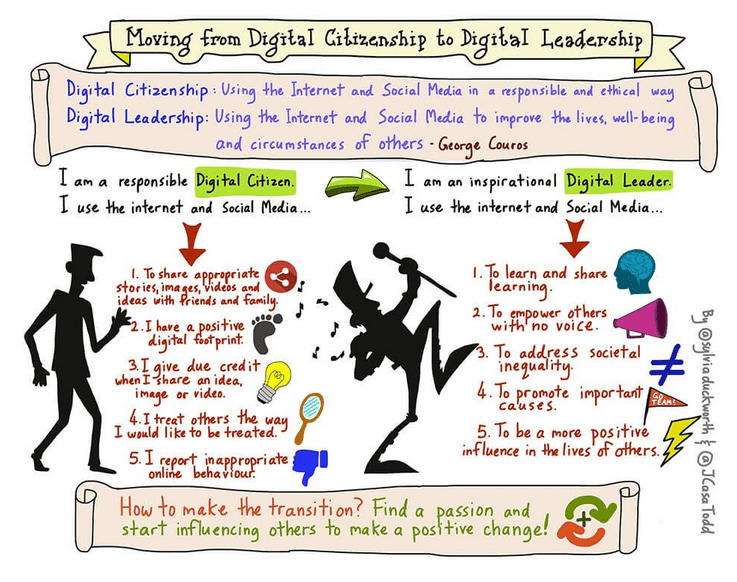
References
Casa-Todd, J. (2016). Rethinking Student (Digital) Leadership and Digital Citizenship [Image]. Retrieved from: https://jcasatodd.com/rethinking-student-digital-leadership-and-digital-citizenship/
Lindsay. J. (2016, July 19). How to encourage and model global citizenship in the classroom. Education Week. Retrieved from http://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/global_learning/2016/07/how_to_encourage_and_model_global_citizenship_in_the_classroom.html
Chen, E., Orth, D. (2013). The strategy for digital citizenship. NAIS Independent School Magazine (online) http://www.nais.org/Magazines-Newsletters/ISMagazine/Pages/The-Strategy-for-Digital-Citizenship.aspx.
14 DLE Digital Citizenship ‘Issues’ (ETL523 Module 2)

Digital Learning Environments (DLE) and digital citizenship implementation have a few issues and dilemmas that must be considered by teacher librarians, and all educational stakeholders:
- Lack of growth mindset: Educators are often reluctant to change. We expect students to have an open mind to proactively embrace new things and attempt to connect to personal learning networks – and recognise that, generally, failure is a part of learning. We expect 21st century learners to be quick to learn and be resilient, yet we ourselves are sometimes close minded, reactive, afraid to fail, and stuck in ruts and ‘old’ methods or tools – as teacher librarians, we must lead in professional reflection, respond to needs and initiate change, particularly in terms of individualising learning plans and environments and recognising that the ways students access information is much different than what it once was (Cooke, 2012).
- Communication via DLE is different: We must tailor the methods and means by which we communicate to ensure that we are understood and authentic. Communication in an DLE is different to face to face communication in terms of turn taking, online digital footprints or identities may not be authentic, the level of commitment or willingness to behave ethically vary understanding and clarity can be varied or blurred, and community expectations are different (Cooke, 2012).
- Lack of thought into quality control: While there are several methods for measuring teacher quality in recent times, there is no official one way to measure the quality of DLE Digital citizenship lessons or teacher / teacher librarian quality (Cooke, 2012). (NOTE: In fact, 21st century learning skills are themselves very difficult to assess and measure in students. We need to find or design one agreed way of measuring quality teaching!)
- Varied degrees of self-regulation, motivation, & overwhelmed, or distracted students: DLE education is often asynchronous or self directed (Cooke, 2012) relying on a student’s ability to self-regulate and motivate. This is sometimes problematic, not only because of individual student ability levels but also because the DLE can be overwhelming, or a place of distraction or ambiguity (see #14).
- Lack of a fluid community of practice or PLNs: Wenger (p.2, 1998, in Cooke 2012) specifies 3 dimensions of a community of practice: 1. they are joint enterprises, created and maintained by their members, 2. they feature mutual engagement with all members joining to form a social entity, and 3. members have a shared store of resources and sensibilities that have been communally developed. However, Wenger (p.6, 1998, in Cooke 2012) does caution that communities of practice should take care not to become insular, rather they should attempt to remain ‘dynamic and fluid.’ (NOTE: I have discussed the concept of a community of practice at length in other blog posts: 1 or 2– see tags also).
- Content at the cost of engagement and application: Stagnant, repetitive, standardised education, subjects and content are still taught in isolation from each other. Memorising facts and clerical tasks are still, despite being the 21st century, generally considered more important than engaging lessons that link to or apply to real life situations – students should be learning by doing rather than by being told (Wheeler, 2015). (NOTE: Would you rather be treated by a ‘doctor’ who learned medicine by reading about it or would you rather be treated by a doctor who has actual experience treating patients?)
- Critical thought is not taught or supported: Inquiry learning and learning through questioning is still not the preferred method of teaching, ill-preparing students for their ‘why’ and ‘how to’ (rather than ‘what’) futures (Wheeler, 2015). “Critical thinking, flexibility, working collaboratively, and creative problem solving are all key components for success in changing environments. But ‘knowing that’ and ‘knowing how’ will not be enough. Students also need to know why” (Wheeler, 2015, Ch.6, p.9).
- Educators have all the say: According to Wheeler (2015), instead of taking a ‘flipped classroom’ approach where learning is student led, the majority of educators are still deciding the curriculum and delivery of the content, delivering lessons with one way dialogue and lack of conversation. This means that students can become disengaged, disconnected and disempowered from their own learning (Wheeler, 2015). It is crucial that we design engaging lessons and topics and use varied learning approaches in order to promote the ability in students to generate their own ideas and voices (rather than copying the voices of others) (Williamson & McGregor 2011). (NOTE: How many of us consider ourselves facilitators of student learning? I myself have it in my teaching and learning philosophy…Time to put this into action!)
- Lack of digital literacy: as per my previous blog post on Information Literacy and Inquiry Based Teaching: ‘According to the ALA, (2016) we must help our students become information literate individuals who can: “determine the extent of information needed; access the needed information effectively and efficiently; evaluate information and its sources critically; incorporate selected information into one’s knowledge base; use information effectively to accomplish a specific purpose; and understand the economic, legal, and social issues surrounding the use of information, and access and use information ethically and legally” (ALA 2016). This is expanded into Digital Literacy by Stripling (2010) who writes: “Digital literacy, itself, is not enough preparation, however, for our students to thrive in today’s global, information-driven world. Students must also acquire the skills of digital inquiry: connecting ideas to personal interests and a desire to know, asking questions that probe beyond simple fact gathering, investigating answers from multiple perspectives, constructing new understandings, expressing the new ideas through a variety of formats, and reflecting on both the process and product of learning” (p16).
- Constantly evolving trans-literacy (multi-literate) expectations: educators must be able to prepare students to evaluate, access and effectively, ethically and legally utilise a variety of resources and tools across a variety of platforms (Preble, 2013; Wheeler, 2015, p.175).
- The digital divide (as discussed in my previous blog post): the digital divide is closely related to Socio-Economic Status and is not just a lack of access to technological devices or internet, but it is also a lack of the ability to utilise technology, inability to produce content, and/or the lack of the ability to apply digital information and skills to real life applications (Jenkins, Clinton, Purushotma, Robison & Weigel, 2006; & Schradie, 2013). (NOTE: this is something imperative for educators to be reflecting upon NOW during this COVID-19 crisis: the digital divide is real and it has an impact on our students whether they are in lockdown or not! Schools MUST CREATE A PLAN for access to and for digital literacy for all students).
- Confusion, panic and lack of policy regarding intellectual property, copyright, fair use and Creative Commons: Educators must create a policy for intellectual property, copyright, fair use and Creative Commons. Thus, we must create guidelines at whole-school level that promote intellectual honesty and respect for the work of others as an ingrained community value (Williamson & McGregor 2011, p17). Educators must then model and teach deeper digital citizenship knowledge and understanding of what can be used, re-used, and shared in items produced electronically, based on an age appropriate teaching sequence (such as teaching students how to locate key words and write bulleted notes before paraphrasing quotes, as suggested by Williamson & McGregor, 2011).
- Safety in the DLE: The DLE requires educators to help students be aware of safety issues such as cyberbullying, creating a work/life balance, age-inappropriate online communications (eg adult images, videos, ads or ‘chats’). (NOTE: The Australian Government have an e-safety page that is particularly relevant and offers resources to educators). However, we must also teach students how to use social media platforms responsibly (Elkin, 2013; Murray, 2013).
- Lack of content curation, aka overwhelmed due to ‘filter failure’ or narrowed view due to ‘filter bubbles’: We must consider how we curate information within our personal learning networks (see #5), and model and teach students how to evaluate the methods for curation so that they aren’t either overwhelmed due to filter failure or creating a narrow world view due to over-stringent filters that act as ‘filter bubbles.’ (Crowdspoke. (2011, June 7).“good curation tools are those that allow you to: Aggregate and gather web pages specific to the topic; Filter content allows the curator to select the best material; Publish to your collection with ease; Share, syndicate and distribute to your audience and the wider community; Allow the curator to edit and add comments as well as providing a comment stream for the audience to nurture discussion around the article; Analytics so you can track the usage of the site; An export facility or a way to back up the curated work” (Adapted from De Rossi, L.C. and Good, R. 2010).
-
11 further ideas on what to think about from lecturer, Julie Lindsay (in ETL523):
- Have we clearly identified our context (eg k-12 NSW Public School in x suburb…)?
- Do we have a shared vision?
- How can we create personalised learning spaces linked to learning needs?
- Have we considered: Hardware / software / networking access?
- Have we considered: Understanding / experience access?
- Do we know our students’ and teachers’ individual digital profiles?
- Are the tools in our ‘digital tool kit’ age appropriate?
- What evidence are we using to determine best practice for online, topical, or connected learning?
- Do all stakeholders have shared understandings, policies or guidelines?
- Is there a PD program or plan to continually evaluate and support the changing environment (eg. do teachers model the digital citizenship behaviours they expect or teach)?
- How will this be shared and networked within a global professional network(s) and local context(s)?
References:
ALA (2016). Information Literacy Competency Standards for Higher education. Retrieved from: https://alair.ala.org/handle/11213/7668
Cooke, N. A. (2012). Professional development 2.0 for librarians: developing an online personal learning network (PLN). Library Hi Tech News, 29(3), 1-9.
Crowdspoke. (2011, June 7). Understand collective curation in under 90 seconds. http://youtu.be/eW775HIlVMg.
Elkin, Susan. (2013, January 1). It’s vital we teach social networking skills in school. http://www.independent.co.uk/voices/comment/its-vital-we-teach-social-networking-skills-in-school-8434531.html
Jenkins, H., Clinton, K., Purushotma, R., Robison, A. J., & Weigel, M. (2006). Confronting the challenges of participatory culture: Media education for the 21 st century. MacArthur Foundation Publication.
Murray, T. (2013, January 7). 10 steps technology directors can take to stay relevant. http://smartblogs.com/education/2013/01/07/the-obsolete-technology-director-murray-thomas/.
Preble, L. (2013, September 14). Nancy Pearl explains transliteracy. http://youtu.be/pNBlzCMq994.
Schradie, J. (2013, April 26). 7 myths of the digital divide. http://thesocietypages.org/cyborgology/2013/04/26/7-myths-of-the-digital-divide/.
Stripling, B. (2010). Teaching students to think in the digital environment: Digital literacy and digital inquiry. School Library Monthly, 26(8), 16-19.
Wheeler, S. (2015). Learning with ‘e’s: Educational theory and practice in the digital age. Crown House Pub Ltd. (Chapter 6: A 21st Century Curriculum). Retrieved from ProQuest
Williamson, K., & McGregor, J. (2011). Generating knowledge and avoiding plagiarism: Smart information use by high school students. School Library Media Research, 14.
Digital Citizenship in the Curriculum (ETL523 Module 1)

21st Century learning and COVID-19 – catalysts for change:
 With the COVID-19 lockdown, the Digital Learning Environment (DLE) issues are relevant like never before. Teachers who have been allowed to stick to their paper programs, regurgitating content from previous classes that they’ve taught or from purchased sources and shying away from digital tools and applications, must now think on their feet to create online programs to suit their classes and individual students.
With the COVID-19 lockdown, the Digital Learning Environment (DLE) issues are relevant like never before. Teachers who have been allowed to stick to their paper programs, regurgitating content from previous classes that they’ve taught or from purchased sources and shying away from digital tools and applications, must now think on their feet to create online programs to suit their classes and individual students.
The Digital Education Advisory Group, approximately 8 years ago, wrote: “What is now required is a catalyst intervention to bring into recognisable focus the change that the whole community will recognise and welcome as transformation that shapes our future” …”We need to harness the transformative potential of digital technology to support new approaches to innovative learning centred around the development of 21st Century Learning skills. These include creativity and innovation; critical thinking, problem solving, decision making; life-long learning; collaboration and communication; ICT literacy; consciousness of being a local and global citizen; and personal and social responsibility” (Digital Education Advisory Group – DEAG, no date).
“Assuming a world in which the welfare of the young people and the economic health of a society and the political health of a democracy are the true goals of education, I believe modern societies need to assess and evaluate what works and what doesn’t in terms of engaging students in learning. If we want to do this, if we want to discover how we can engage students as well as ourselves in the 21st century, we must move beyond skills and technologies. We must explore also the interconnected social media literacies of attention, participation, cooperation, network awareness, and critical consumption” (Rheingold, 2010 p.24; emphasis added).
“Schools need not only to prepare students to be responsible citizens, but also to prepare them with the technological and communicative skills necessary to engage civic responsibility in a digital age” (Richards, 2010, p.520).
Teacher ability:
It takes a village: I wholeheartedly subscribe to the notion presented by Hollandsworth, Dowdy, & Donovan, (2011) that educators have a duty of care for student safety and security, educational enhancement, ethical and legal behaviours and becoming an effective member of communities, in both the physical and digital environment through policy, leadership and practice.
It does, indeed, ‘take a village to raise a child’ to be a good global and digital citizen, and this process should include all stakeholders: parents, teachers, teacher librarians, administrators, academics, technology professionals and, none the least of which, students. This means that educators must be proactive in effective digital citizenship DLE (including risk awareness et al), as well as in fostering student peer mentor programs, effective student role models, and quality educational faculty/staff DLE ability.
PLC, PLN, PLE, DLE: Furthermore, we as educators need to foster professional learning communities (PLC) through culture of personal learning networks (PLN) and personal learning environments (PLE), including networks within the Digital Learning Environment (DLE) according to ‘Steve Wheeler on future learning environments: professional, powerful and personal’ (YouTube / 2:09 mins) | https://youtu.be/db9PXLqoduQ
Creation of content:
There are some great resources for creating content, as recommended by ETL523 Module 1, including:
- https://www.commonsense.org/education/
- https://globaldigitalcitizen.org/
- http://www.newmedialiteracies.org/our-space-being-a-responsible-citizen-of-the-digital-world/
Just as most schools have created a school ‘code of conduct’, so too should they proactively (rather than reactively) teach a DLE ‘code of conduct’ (Hollandsworth, et al, 2011). And just as we review and evaluate the quality of our lesson content and physical curriculum, so too should educators have a structured means in which to create, deliver and then evaluate their online DLE digital citizenship curriculum. (I like the ‘writing on the bathroom wall’ analogy, which links toilet graffiti to the banter and issues that sometimes arise in social media platforms or chats-we should have a plan for how to help students handle these situations in both environments as neither are able to be fully policed or ‘filtered’ by adults). A great source of raising awareness in students are the Pause and Think by Commonsense Education.
In terms of ways to teach digital footprint ideas to students, I particularly like the videos by Everyone – Think before you post, and the blog post by Nielsen (2011), Discover what your digital footprint says about you.
Furthermore, we need to reconsider the curriculum and how we have created and delivered content in the past: “For educators and the schools in which they teach, the challenges of this moment are significant. Our ability to learn whatever we want, whenever we want, from whomever we want is rendering the linear, age-grouped, teacher-guided curriculum less and less relevant.” (Richardson, 2008, Emphasis added).
Brown, Dehoney and Milichap (2015) surmise that the core dimensions of Next Generation Digital Learning Environment (NGDLE) are:
- Interoperability and integration
- Personalisation
- Analytics, advising and learning assessment
- Collaboration
- Accessibility and universal design
Lindsay & Davis’ (2012) ‘enlightened digital citizenship model’ recommends we consider digital citizenship in terms of four areas of content:
- Safety and privacy
- Etiquette and respect
- Learning habits – workflow
- Literacy and fluency
Social media / Digital footprints (safety / privacy / brand):
We all have a digital footprint and we must model and teach an awareness of this to students. I agree with Richards (2010) who points out that we either teach students how to engage in social media responsibly, or risk them attempting it on their own, which is very much in line with research on sexual reproduction education. Wheeler equates learning about the internet to learning how to cross the road safely – what better place to teach these concepts than in school? (Wheeler, 2015, p.176).
I think it is imperative that this education begins prior to students having a substantial digital footprint, adhering to guidelines like ‘no facebook until you are 13’ – because teaching them to be mindful of what they display digitally after they have already begun displaying themselves, is like trying to teach someone who has just voted in a political election, how to vote. We must teach them early on how our digital footprint or identity is now our (online) personal ‘brand.’
We are identified at home in one way, at work or school in one way, and online or digitally in one way and our identities change through the passage of time. People can forget or not know anything about your identity in the real world, but in the digital environment, your identity is more permanent. Furthermore, the 21st century boundaries between these contexts are now blurred. We need to ask our students and them how to recognise ‘what is your identity?’ across these three platforms and throughout time.
We must therefore consider that students (and teachers) need to be literate in (aka be able to have understanding access) social media, which requires: attention, participation (civil or otherwise), collaboration, network awareness and critical thought (or critical ‘consumption’) as according to Rheingold, H. (2010).
 Something else to consider is that we have an expectation that students will be capable of digital citizenship, when their understanding of citizenship overall is still developing, particularly at the K-6 level. We must be aware of the way that we have learnt citizenship in the face to face world and how 21st Century learners have not had the same face to face opportunities and foundations that we’ve had. They must learn citizenship face to face and digitally simultaneously…like learning two different languages at the same time! Furthermore, social networks and social media have played a significant part in changing citizenship and previous boundaries and accepted expectations for social behaviour. Some face to face social constructs (such as body language) are not relevant in the digital social environment and as a result, effective use of emoticons or gifs or memes have been created to fill the void.
Something else to consider is that we have an expectation that students will be capable of digital citizenship, when their understanding of citizenship overall is still developing, particularly at the K-6 level. We must be aware of the way that we have learnt citizenship in the face to face world and how 21st Century learners have not had the same face to face opportunities and foundations that we’ve had. They must learn citizenship face to face and digitally simultaneously…like learning two different languages at the same time! Furthermore, social networks and social media have played a significant part in changing citizenship and previous boundaries and accepted expectations for social behaviour. Some face to face social constructs (such as body language) are not relevant in the digital social environment and as a result, effective use of emoticons or gifs or memes have been created to fill the void.
Delivery of content:
In order to deliver the content or curriculum, the devices and tools chosen must be convenient, consistent, and allow for frequent access to digital devices (Mann, 1999; Kelley & Ringstaff, 2002; NCES, 1999; and Statham & Torrell, 1999, in Kemker, 2005).
Having access to physical technology (primarily due to SES) is not the only issue. As pointed out by Jenkins, Clinton, Purushotma, Robinson & Weigel (2006), teachers who wish to obtain full involvement of their students by creating a ‘participatory culture,’ must also make adjustments to their pedagogy based on:
- Individual student ability to participate in the DLE given their varied access to opportunities, experiences, skills and knowledge,
- The varied degrees of understanding media transparency (or lack thereof) around how media shape world views, or how to apply filters for the large number of ‘hits’ or ‘tweets’ or emails that one receives so as to not become overwhelmed,
- and the varied degrees of understanding, training or socialisation of digital citizenship or ethical expectations for global DLE success.
 (Note to self: The issue of access to the internet, devices, applications and digital or social media tools in terms of Socio Economic Status and individual choice was covered in ETL401 and ETL503 and in my blog posts for those courses).
(Note to self: The issue of access to the internet, devices, applications and digital or social media tools in terms of Socio Economic Status and individual choice was covered in ETL401 and ETL503 and in my blog posts for those courses).
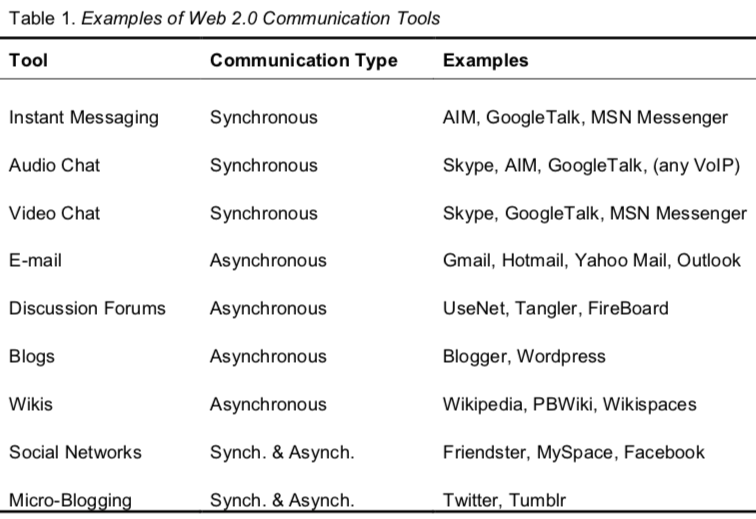
Furthermore, we must plan whether our delivery will be synchronous or asynchronous (or a mixture of the two): “Synchronous discussion is real-time or live communication that takes place on platforms such as instant messengers, audio chat, or video chat. Asynchronous discussion is non-live communication that takes place over time and includes platforms such as e-mail, discussion forums, blogs, and wikis” (Richards, 2010, p.516).
Evaluation & quality control:
Digital learning spaces need to be created in conjunction with digital citizenship awareness and incorporating essential attitudes and skills needed to be a productive (digital) learner . However, this means that digital citizenship is not just about recognising online copyright laws, or keeping students safe online. (See my previous post What is digital citizenship?).
Quality tools, lessons (either face to face or digitally) should enable students to be engaged in authentic tasks, connected to the real world, involving all partners of the learning community such as teachers, students, parents, business partners, and higher education experts (Kemeker, 2005). But, what can we use to measure student engagement and connectedness to ensure they are fully active, creative and ethical DLE participants?
Jenkins, et. al. (2006) have a comprehensive list of skills and competencies:

Prior to the DLE, quality standards, each with a scale of 1-5, were created by Newmann and Wehlage (1993) to help teachers assess the “authenticity” of classroom tasks and experiences, Newmann and Wehlage (1993): 1. Higher order thinking, 2. Depth of knowledge, 3. Connectedness to the world beyond the classroom, 4. Substantive conversation, and 5. Social support for student achievement – which is closely linked to the more expanded and also individually scaled from 1-5 Quality Teaching Framework (Gore, 2018):
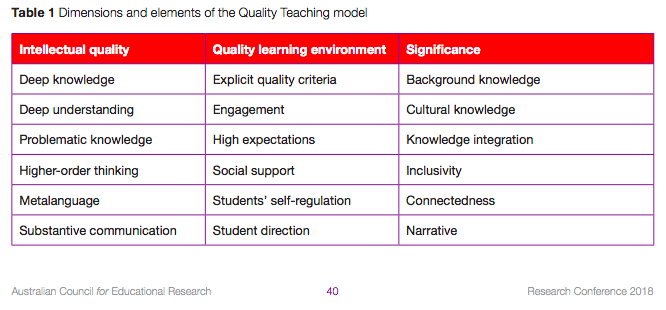

I think it is important to consider quality teaching and leadership standards within the context of the DLE, as well as the skills and competencies from Jenkins et al (2006) and possibly the 21st Century Learning skills identified from various sources (see previous blogs via tags).
References
Brown, M., Dehoney, J., & Millichap, N. (2015). The next generation digital learning environment. A Report on Research. ELI Paper. Louisville, CO: Educause April.
Digital Education Advisory Group. Beyond the classroom: A new digital education for Australian’s in the 21st Century. Retrieved from https://docs.education.gov.au/system/files/doc/other/deag_final_report.pdf
Gore, J. (2018). Dimensions and Elements of the Quality Teaching Model. [Image]. Australian Council for Educational Research – Research Conference 2018. Retrieved from https://research.acer.edu.au/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1336&context=research_conference
Hollandsworth, R., Dowdy, L., & Donovan, J. (2011). Digital citizenship in K-12: It takes a village. TechTrends, 55(4) 37-47.
Jenkins, H., Clinton, K., Purushotma, R., Robison, A. J., & Weigel, M. (2006). Confronting the challenges of participatory culture: Media education for the 21st century. MacArthur Foundation website https://www.macfound.org/media/article_pdfs/JENKINS_WHITE_PAPER.PDF
Kemker, K. (2005). The digital learning environment: What the research tells us. Apple White Paper. Retrieved from (see link).
Lindsay, J., & Davis, V. (2012). Flattening classrooms, engaging minds: Move to global collaboration one step at a time. Allyn and Bacon. Chapter 5: Citizenship. (available on CSU DOMS as a downloadable PDF)
Rheingold, H. (2010). Attention and other 21st century social media literacies. Educause Review 45(5). Retrieved from http://www.educause.edu/ero/article/attention-and-other-21st-century-social-media-literacies
Nielsen, L. (2011, August 19). Discover what your digital footprint says about you. Retrieved from http://theinnovativeeducator.blogspot.com/2011/08/discover-what-your-digital-footprint.html
Richards, R. (2010). Digital citizenship and Web 2.0 tools. Journal of Online Learning and Teaching, 6(2), 516-522. Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/7740/fb40e7030935d7b00d5bd07a19ba83c496ff.pdf
Richardson, W. (2008, December 3). World without walls: Learning well with others. Edutopia. Retrieved from http://www.edutopia.org/collaboration-age-technology-will-richardson.
Wheeler, S. (2015). Learning with ‘e’s: Educational theory and practice in the digital age. Crown House Pub Ltd. Chapter 12: Literacy in a connected world.
What is Digital Citizenship?

Before I fully delve into the ETL523 Digital Citizenship content, I need to briefly determine what I think digital citizenship is, in terms of being an educator of (young) children.

Digital citizenship is primarily an add on to citizenship. We must behave in a civilised manner in life, both face to face (citizenship) and online/electronically (digital citizenship). If at first students have no concept of citizenship
– that is, a communal bond and respect for living and working harmoniously together for the greater good –
then they will similarly have no concept of digital citizenship (living and working harmoniously together for the greater good electronically).
Positive Behaviour for Learning (PB4L), Social Emotional Learning (SEL), citizenship/ethics should be integral to every aspect of our 2020 teaching day. We must help students regulate through consistent SEL, relate to them via whole school programs like PB4L, so that we may reason / rationalise with them with lessons on citizenship and ethics (these being Dr Bruce Perry’s 3 R’s as provided by Beacon House, 2020).
Furthermore, I would add that as teachers our rationalisations / lessons must all be able to be reflected upon and evaluated and revised continually using some form of collegial quality teaching standards, such as the Quality Teaching Framework (QTF)…perhaps this could be my contribution to ETL523, to link Digital Learning Environments to the QTF…
The below notes are from reading ETL523 Module 1 ‘What is digital citizenship’:
Digital citizenship therefore, is not just about keeping students safe online, or giving students the skills or devices to access technology. It is helping students become productive members of an digital (learning) environment…digital citizens of a globally digital social society. This is supported by the video by ISTE, (2018) Rethinking digital citizenship.
Furthermore, as detailed by Greenhow (2010), Ribble, Bailey, and Ross (in their book, Digital Citizenship in Schools, ISTE, 2007), consider the 9 elements of digital citizenship to be: digital etiquette, digital communication, digital access, digital literacy, digital commerce, digital law, digital rights and responsibilities, digital health and wellness, and digital security.
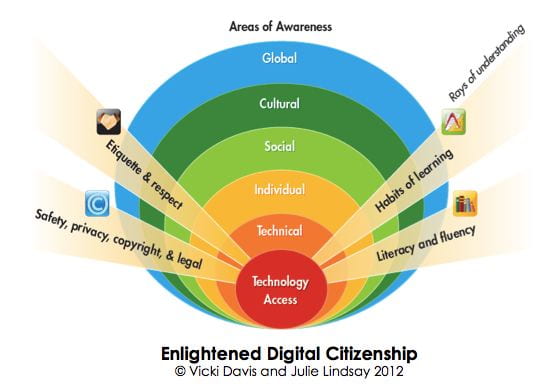
Digital citizenship requires technical, individual, social, cultural and global awareness, which must be considered by teachers in the practical terms of students’ understanding the concepts of: safety, privacy, copyright, fair use and legal compliance, etiquette and respect, habits of learning (responsible, reliable management of online activity), literacy and fluency. This is best demonstrated by the Enlightened digital citizenship model of Davis & Lindsay (2012):
References
Beacon House, (2020). Dr Bruce Perry’s 3 R’s. Retrieved from https://beaconhouse.org.uk/resources/
Greenhow, C. (2010). New concept of citizenship for the digital age. Learning & Leading with Technology, 37(6), 24-25.
ISTE. (2018, October 11). Rethinking digital citizenship. Retrieved from https://youtu.be/iwKTYHBG5kk.
Lindsay, J., & Davis, V. (2012). Flattening classrooms, engaging minds: Move to global collaboration one step at a time. Allyn and Bacon. Chapter 5: Citizenship. (available on CSU DOMS as a downloadable PDF)
Merriam-Webster, (2020). Definition of Citizenship. [Image]. Retrieved from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/citizenship
![Hague, C., & Payton, S. (2010). Digital literacy across the curriculum [Handbook [Image]. pp. 19.](https://thinkspace.csu.edu.au/croe/files/2020/05/Hague-C.-Payton-S.-2010.-Digital-literacy-across-the-curriculum-Handbook-Image.-BECTA-FutureLab.-pp.-19.-National-Foundation-for-Educational-Research-httpswww.nfer_.ac_.uk-publicationsFUTL06FUTL06.pdf.png)
